Treatment of Diastasis Recti
Diastasis recti is not a cosmetic defect, but an anatomical disorder in which the connective tissue weakens and the muscle fibers separate along the linea alba. This condition occurs in women after pregnancy and childbirth, and in men due to chronic stress, weight gain, or poor exercise habits. Successful recovery requires an accurate diagnosis, an understanding of the causes of the separation, and the participation of experienced specialists: surgeons, rehabilitation therapists, and exercise therapists.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Causes of diastasis

The main cause is the loss of elasticity of the connective tissue of the aponeurosis, which holds the muscles along the linea alba. Factors that cause stretching and divergence of the structures:
- Pregnancy – hormonal changes and abdominal enlargement place excessive stress on the anterior abdominal wall.
- Heavy physical exercise without preparation.
- Weight lifting in men.
- Overweight and obesity.
- Congenital weakness of the connective tissue.
- Frequent pregnancies or multiple pregnancies.
- Abdominal wall trauma and surgery.
In men, diastasis can occur due to chronic abdominal tension, coughing, and overexertion from sports. In women, the pathology most often manifests after childbirth, when the tissue has not yet had time to recover, and stress has resumed.
Classification and degrees of diastasis

Doctors distinguish three degrees of pathology, depending on the width of the diastasis divergence:
- Grade I – divergence up to 2 cm. This is a mild condition, often found in women after their first childbirth or with moderate exertion. It can be treated with exercise.
- Grade II – divergence from 2 to 5 cm. The abdomen protrudes noticeably, the anterior abdominal wall is weakened, and pain may occur.
- Grade III – more than 5 cm, the muscles do not close, the diastasis is thinned, and surgery and diastasis suturing are often required.
This classification helps the doctor determine which treatment method – conservative or surgical – will be effective. Often, the pathology develops gradually, so early diagnosis and monitoring are the best way to avoid surgery.
Symptoms of diastasis recti
The main symptom is a bulge or "roll" along the linea alba, especially noticeable with muscle tension. Sometimes, a soft separation between the muscle edges can be felt upon palpation, which intensifies with coughing or lifting the head. In women, this symptom most often appears after pregnancy, when the connective tissue has not yet regained its strength, and in men, after intense exercise or heavy lifting.
Significant muscle separation can lead to an umbilical hernia, and in severe cases, abnormal positioning of internal organs. It is important to remember that self-diagnosis of the degree of diastasis is inaccurate in 80% of cases; professional diagnosis by a doctor is necessary.
Additional signs:
- A feeling of distension or a nagging pain in the abdomen
- Weakening of the muscular corset, a "collapse" of the anterior abdominal wall
- Deterioration of posture and the appearance of lower back pain
- Digestive problems due to changes in intra-abdominal pressure
- After surgery or childbirth – slow scar healing, a feeling of instability
Treatment methods for diastasis
Conservative Treatment
In the early stages of diastasis, when the discrepancy does not exceed 2-3 cm, a comprehensive conservative program becomes the basis of therapy.
This includes:
- An individually tailored course of therapeutic exercise
- Physical therapy procedures to strengthen connective tissues
- Wearing a support bandage
- Diet and weight management
- Teaching proper breathing and movement habits
The goal of therapy is to strengthen the abdominal muscles and reduce stretching of the aponeurosis. Particular attention is paid to the transverse abdominis muscle, which is responsible for stabilizing the anterior abdominal wall. It forms an internal "corset" and helps restore tone to weakened tissues.
Important: Regular abdominal exercises (crunches, leg lifts, planks) are contraindicated for diastasis recti – they increase pressure and can worsen the separation. A doctor or rehabilitation instructor will select gentle techniques aimed at activating the deep muscles without overexerting the straight line.
The results of conservative treatment are gradual: improved posture, reduced protrusion, and pain relief. However, with a significant defect in the connective tissue aponeurosis, it is impossible to completely correct the diastasis without surgery.
Physical Exercises and Rehabilitation
Physiotherapists at the K+31 Clinic emphasize that restoring muscle tone and strengthening the anterior abdominal wall is only possible with regular and proper exercise. The main goal of the exercises is to engage the deep abdominal muscles and restore proper intra-abdominal pressure.
Basic principles of rehabilitation:
- Diaphragmatic breathing. When inhaling, the abdomen expands, and when exhaling, it is drawn toward the spine. This improves circulation and strengthens connective tissue.
- Vacuum exercise. When exhaling, the abdomen is drawn in, stimulating the transverse abdominal muscle.
- Smooth movements, without jerking. It is important to avoid raising the torso and overexerting the rectus abdominis.
- Gradual increase in load. After childbirth or surgery, exercises are introduced gradually, under the supervision of a specialist.
- Posture management. Incorrect spinal alignment increases stress on the linea alba and slows recovery.
Rehabilitation programs may include myostimulation, massage, and kinesiotaping. For moderate diastasis, these methods produce significant results, especially if treatment is started in the first months after childbirth.
For men whose diastasis is caused by physical activity or obesity, the emphasis is on normalizing weight, strengthening the transverse muscles, and stabilizing the lumbar spine.
Surgical Treatment
If the discrepancy exceeds 4–5 cm or a hernia is present, surgery—diastasis closure—is indicated. This is the only way to restore normal abdominal wall anatomy in cases of severe pathology.
Modern surgery utilizes several correction methods:
- Aponeurosis plication. The most common method involves the surgeon suturing the white line along the midline, returning the muscles to their original position. The suture is made with a strong, non-absorbable material.
- Endoscopic diastasis closure. The surgeon inserts instruments and a video camera through small punctures. This method is minimally invasive, does not require large incisions, and recovery is faster.
- Abdominoplasty with aponeurosis reinforcement. This is used when diastasis is combined with excess skin or after pregnancy. In addition to suturing, abdominal contour correction is performed, improving appearance and eliminating tissue stretching.
- Mesh implant placement. If connective tissue is weakened, a special mesh can be used to strengthen the anterior wall and prevent recurrent dehiscence.
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and lasts 1-2 hours. The patient stays in the hospital for 1 to 3 days, after which the recovery period begins.
Surgical treatment can correct not only the aesthetic defect but also functional impairments: blood pressure is normalized, pain disappears, and the muscular frame is strengthened.
After surgery, it is important to follow recommendations: limit physical activity, wear compression garments, and perform breathing exercises. Failure to follow these recommendations can lead to recurrent dehiscence of the linea alba or weakening of the suture.
Why is diastasis recti best treated at K+31?
The K+31 Clinic is one of the leading surgical and rehabilitation centers in Moscow, using modern diagnostic and suturing methods for diastasis. By choosing K+31, patients receive:
- Experienced specialists. The clinic's surgeons perform dozens of diastasis correction surgeries annually and are proficient in both classical and endoscopic techniques.
- Modern diagnostics. Ultrasound, CT, and MRI of the anterior wall allow us to accurately determine the degree of divergence and the condition of the aponeurosis before treatment.
- Comprehensive approach. Treatment includes consultations with a surgeon, rehabilitation specialist, and physiotherapist. The program is tailored individually, from conservative therapy to surgery.
- Minimal invasiveness. We use small incisions, cosmetic sutures, and modern materials, which shortens the recovery period.
- Comfortable conditions. The inpatient wards are equipped to international standards, and the staff supports the patient at every stage – from diagnosis to discharge.
- On-site rehabilitation. After surgery, the patient undergoes a rehabilitation course under the supervision of the clinic's specialists, eliminating the risk of recurrent diastasis.
At "K+31," special attention is paid to women after pregnancy and childbirth. Doctors help safely restore the abdomen, maintain the aesthetic appearance of the figure, and prevent complications typical of a weakened anterior abdominal wall.
Men who experience diastasis due to exercise or excess weight are offered specialized muscle strengthening and metabolic normalization programs.
Diastasis recti is a common but treatable condition. It's important not to ignore the symptoms: the sooner diastasis is diagnosed, the higher the chance of avoiding surgery and maintaining the health of the anterior abdominal wall.
Treatment at the K+31 clinic combines medical precision, an expert approach, and a commitment to patient comfort. Here, we help you regain not only a flat stomach but also your body confidence – safely, reliably, and under the supervision of top surgeons.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services









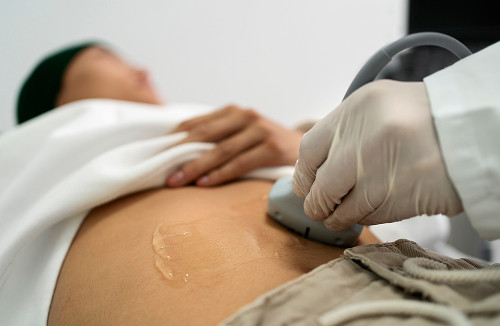






































































What is diastasis recti?
Diastasis recti is a condition in which the connective tissue that holds the rectus abdominis muscles in the center of the abdomen weakens, creating a gap between them. The linea alba stretches, and the anterior abdominal wall loses its density. A longitudinal bulge appears, becoming noticeable when the abdominal muscles are engaged. This isn't just a cosmetic issue: weakened muscles affect posture, create discomfort, and can lead to hernia formation.
Over time, diastasis recti can progress if the muscles aren't strengthened and intra-abdominal pressure isn't balanced. The earlier the condition is diagnosed and treated, the higher the chance of restoring a natural abdominal shape without surgery.