Treatment of Uterine Prolapse
Uterine prolapse is a common problem faced by many women, especially after childbirth and with age-related changes. This pathological condition not only impairs quality of life but can also lead to serious complications.
Thanks to modern diagnostic and treatment methods used at the K+31 Clinic in Moscow, genital prolapse can be effectively treated and quality of life restored. In this article, we will examine in detail all modern methods of genital prolapse correction and their use at different stages of the condition.
To clarify the cost of treatment and learn about the methods that can be used in your case, schedule a consultation with a doctor!

specialists

equipment

treatment
Symptoms of uterine prolapse
Uterine prolapse can present differently depending on its severity. In the early stages, symptoms are mild, but as the condition progresses, they worsen.
The main signs of prolapse are:
- Heaviness or pressure in the lower abdomen
- Vaginal discomfort and aching pain radiating to the lower back
- Feeling of a foreign body in the perineum
- Frequent urination, urinary incontinence when coughing, sneezing, or laughing
- Problems with urination
- Pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Bleeding not related to menstruation
Symptoms may worsen with physical activity and decrease when lying down. If such symptoms appear, it is important to consult a gynecologist for diagnosis and treatment.
Methods for diagnosing uterine prolapse
History taking
Collecting anamnesis is the first and very important step in diagnosing uterine prolapse. Allows you to identify risk factors, analyze the duration and dynamics of symptom development, assess the impact of prolapse on the patient's quality of life, and suspect concomitant pelvic disorders.
Key aspects when collecting information about the patient's condition:
- Obstetric and gynecological history: information on the number and course of births (natural or cesarean section, presence of ruptures, fetal weight), past perineal trauma, gynecological surgeries.
- Complaints and symptoms.
- Risk factors: heavy physical labor, heavy lifting, chronic constipation, prolonged cough, obesity, hereditary connective tissue weakness.
- Impact of the disease on quality of life: limitation of physical activity, social maladjustment (for example, fear of urinary incontinence), or psychological discomfort.
A detailed history helps differentiate prolapse from other pathologies, determine the need for additional research, and choose the appropriate treatment strategy.
Questionnaire and Medical Examination
A patient questionnaire plays an important role in diagnosing uterine prolapse, complements the anamnesis, and allows for a faster assessment of symptoms. Specialized questionnaires are used for this purpose.
After the questionnaire, a medical examination is conducted, which includes several stages. First, a general examination is performed, during which the patient's body type, body mass index, and skin condition are assessed.
Next, a gynecological examination is performed using a speculum. The doctor evaluates the condition of the vaginal mucosa, the position of the uterus, its size, mobility, and the tone of the pelvic floor muscles.
Functional tests play an important role in the diagnosis. The Valsalva maneuver helps determine the degree of protrusion of the organs during straining, the cough test reveals stress urinary incontinence, and the swab applicator test reveals urethral mobility.
Examination is recommended during the first half of the menstrual cycle, as this period allows for better visualization of anatomical structures and reduces the likelihood of tissue swelling.
Ultrasound Diagnostics
Ultrasound is a leading instrumental method for pelvic organ diagnostics. It provides highly accurate visualization of anatomical structures and dynamic assessment during functional testing.
The main ultrasound examination methods are transvaginal, transperineal, and transabdominal ultrasound. A transvaginal examination is performed in a standard position to assess the anatomy at rest, with a mandatory Valsalva maneuver to determine maximum organ displacement. The examination measures the urethrovesical angle, the position of the bladder neck, and the distance from the pubic symphysis to key anatomical structures.
Transperineal ultrasound, especially with 3D/4D technology, allows for visualization of the entire pelvic floor in a single plane, creating volumetric models, and accurately assessing fascial and muscular defects. A transabdominal approach is used as an adjunctive method when there are contraindications to a vaginal examination, as well as to assess concomitant pelvic pathologies.
Ultrasound diagnostics pay special attention to assessing key parameters. Bladder examination includes determining the position of the bladder neck relative to the pubic symphysis, wall thickness, and residual urine volume. When assessing the uterus, the distance from the external os to the pubic symphysis is measured, the angle of its inclination, and the condition of the ligamentous apparatus are determined. For the rectum, important parameters include the depth of the rectovaginal septum and the presence of signs of a rectocele.
Additional Tests
For a comprehensive assessment of pelvic dysfunction and the selection of optimal treatment strategies, the following additional tests are used:
- Proctography: assessment of the anatomy of the rectum and pelvic floor muscles. Performed with contrast during straining.
- Cystography: diagnosis of cystocele and stress urinary incontinence.
- Cystoscopy: helps rule out benign or malignant tumors and cystitis.
- Colonoscopy: indicated for gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Electromyography: assessment of pelvic floor muscle innervation to diagnose neurogenic disorders.
- Laboratory tests: urinalysis, hormonal profile assessment.
- MRI of the pelvis: performed when a detailed assessment of all supporting structures is necessary.
Classification and stages of uterine prolapse
Anatomical classification by involved structures:
- Cystocele: prolapse of the anterior vaginal wall with bladder involvement
- Rectocele: protrusion of the posterior vaginal wall with pressure on the rectum
- Enterocele: prolapse of the vaginal vault with intestinal loops
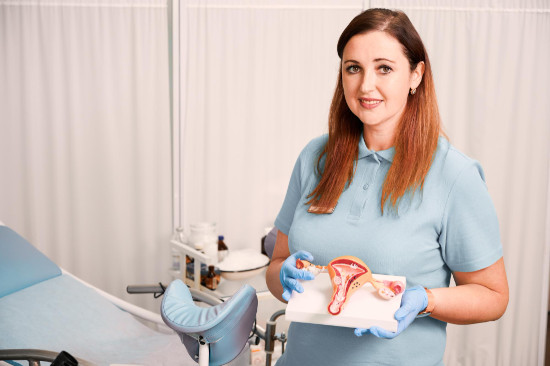
Clinical classification of pathology by degree of prolapse:
- Stage 1 (mild) The prolapse is not visible externally, and symptoms are mild
- Stage 2 (moderate) A "foreign body" sensation may occur, especially when straining
- Stage 3 (severe, incomplete prolapse) Accompanied by severe discomfort, pain, and sexual dysfunction
- Stage 4 (extremely severe) The uterus protrudes completely beyond the vagina. Requires urgent surgical treatment due to the risk of necrosis and infection
Surgical options
Techniques using autologous tissues
Classical surgical techniques for genital prolapse correction using autologous tissues are highly physiological, carry no risk of implant rejection, and have a minimal risk of complications.
Main types of surgical interventions:
- Anterior colporrhaphy: used for cystocele, involves strengthening the anterior vaginal wall using autologous fascial structures.
- Posterior colporrhaphy: indicated for rectocele, restores the integrity of the rectovaginal septum.
- Manchester operation: a combined technique combining colporrhaphy with cervical amputation.
- Sacrospinal fixation: used for posthysterectomy prolapse.
The main advantages of these techniques are the preservation of natural anatomy and the absence of the risk of erosions and infectious complications typical for mesh implants.
Mesh Implant Techniques
Mesh technologies represent the modern standard for surgical treatment of genital prolapse, providing reliable anatomical fixation of the pelvic organs. These techniques are particularly in demand for recurrent prolapse, severe prolapse, multiple pelvic diaphragm defects, and systemic connective tissue dysplasia.
Modern surgical techniques for uterine prolapse correction:
- Anterior/posterior prosthetic implantation: transvaginal placement of Y- or T-shaped systems with fixation to the sacrospinous ligament or obturator membrane. Optimal treatment for cystocele and rectocele.
- Hysteropexy: the "gold standard" for upper vaginal prolapse. The mesh implant is fixed to the anterior longitudinal ligament of the sacrum.
- Total mesh prosthesis: comprehensive restoration of all sections of the pelvic floor.
- Transobturator fixation: minimally invasive correction of stress incontinence.
The main advantages of mesh technologies include high anatomical efficiency, low recurrence rates, the ability to comprehensively correct multiple defects, and preservation of sexual function.
Frequently Asked Questions
We answer the most common questions from our patients.
Can prolapse be treated without surgery?
What exercises are prohibited with prolapse?
Can I give birth with uterine prolapse?
What are the dangers of untreated prolapse?
What is the cost of the surgery?

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services










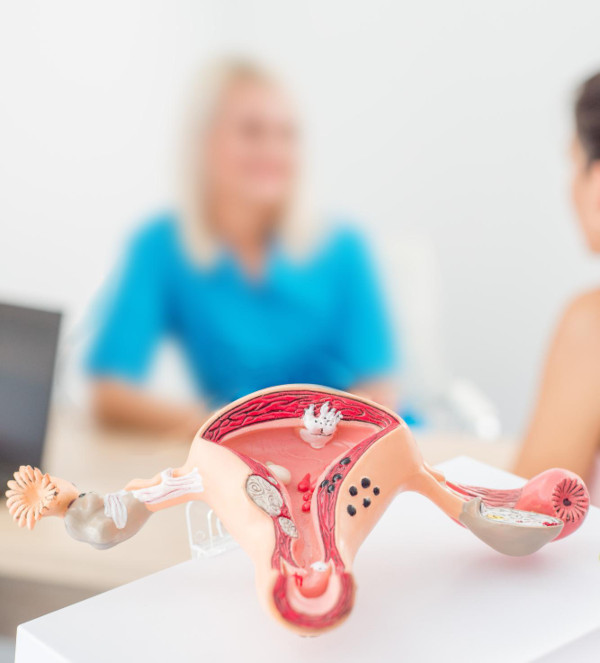
























































Uterine Prolapse: Definition and Causes
Genital prolapse is a pathological condition in which the uterus shifts downward into the vagina due to weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and ligamentous apparatus. Normally, these structures maintain the correct anatomical position of the pelvic organs, but when they are insufficient, the uterus gradually descends under the force of gravity.
Main causes of pathology:
The pathology progresses gradually, so prompt treatment is important to prevent complications.