AV block
The human heart functions through a complex system of electrical impulse generation and conduction. These impulses regulate the rhythm of the atria and ventricles, ensure blood circulation, and deliver oxygen to the organs. AV block is a common pathology that reduces the heart's efficiency, leading to oxygen starvation and nutrient deficiencies. According to statistics, this disorder is diagnosed in 12-15% of patients with cardiovascular disease.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Causes of AV block
The causes of this pathology vary widely, from congenital anomalies to diseases acquired during life.
Congenital heart block
They develop during fetal development due to:
- Structural abnormalities of the cardiac conduction system
- Infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy (rubella, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus)
- Congenital heart defects
- Autoimmune diseases in the mother (Sjogren's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus)
Taking anticonvulsants or antiarrhythmic drugs, and drinking alcohol during pregnancy also increase the risk of developing AV block.

Acquired Blocks
Occur throughout life as a result of:
- Myocardial infarction
- Endocarditis
- Rheumatism
- Age-related changes
- Long-term and uncontrolled medication use
Sometimes the disease develops after cardiac surgery or catheterization.
Classification of AV block
First-degree AV block
This is considered the mildest form of conduction disorder. In this case, all impulses from the atria reach the ventricles, but the propagation velocity is reduced. On the ECG, this is manifested by a prolongation of the P-Q interval exceeding 0.2 seconds. This pathology is often discovered incidentally during routine examinations. In young people and athletes, this indicator is considered normal, especially with high vagal tone. In patients with organic heart disease, the presence of first-degree AV block signals the onset of conduction system damage and requires attention.
Second-Degree AV Block
Some atrial impulses fail to reach the ventricles, resulting in periodic dropped ventricular complexes on the ECG. Depending on the nature of the dropped complexes, there are several types of second-degree AV block:
- Mobitz I. Electrical impulses from the atria are less able to reach the ventricles. The PQ interval lengthens until one of the QRS complexes is dropped. Then the cycle repeats.
- Mobitz II. Some impulses fail to reach the ventricles. The PQ interval remains unchanged, and the QRS complexes are usually wide.
- High-degree incomplete AV block. Not a single electrical signal from the atria reaches the ventricles. This condition is considered life-threatening and requires immediate intervention.
The most dangerous forms are Mobitz II and high-degree block. Often they progress to complete AV block and require the installation of a pacemaker.
Third-degree AV block
Considered the most severe form of conduction disorder, this is a cardiac arrest. The atria operate at a normal rhythm, determined by the sinus node, while the ventricles operate at their own, slow rhythm. On an ECG, this pathology is manifested by a lack of connection between P waves and QRS complexes. The ventricular rate is 20-40 beats per minute.
Which doctor should I see?
At the first sign of AV block, you should consult your primary care physician. Once a heart rhythm disturbance is detected, they will refer you to a cardiologist. If the condition causes sudden weakness or fainting, call an ambulance. If severe AV block is confirmed, a consultation with an arrhythmologist—a specialist in heart rhythm disorders—is required. They will determine the need for a pacemaker and will manage the patient after the device is implanted.

Questions and Answers
Can you live with AV block?
When is a pacemaker necessary?
Can AV block resolve on its own?
How does AV block differ between young and older people?
Can you exercise with AV block?
Is AV block dangerous during pregnancy?
How often should I see a doctor for AV block?

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services









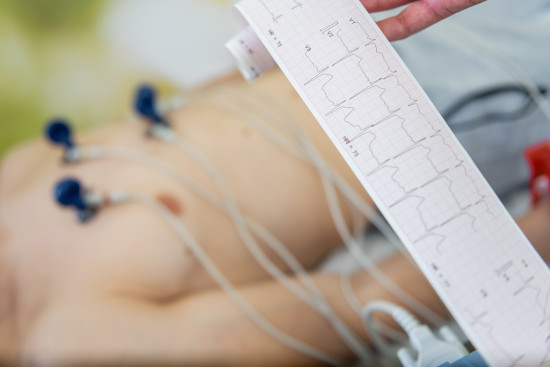

























































General information about atrioventricular block (AVB)
AV block is a disruption in the conduction of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles. Normally, the signal from the sinus node passes through the AV node and then along the conduction system, causing the ventricles to contract. With AV block, this process slows down or stops completely.
Treatment for AV block is available at the K+31 Clinic in Moscow. Experienced doctors use modern equipment, ensuring safety and high precision. They also regularly consult with patients on nutrition, physical activity, and risk factor management to reduce stress on the heart. This comprehensive approach provides not only treatment but also long-term support for cardiovascular health.