Spinal Compression Fracture
Approximately 100 people per million people worldwide experience spinal injuries each year. Compression fractures account for a significant portion of these injuries. Spinal injuries can lead to serious consequences such as limited mobility and even disability, so the intervention of a competent specialist in such situations cannot be overstated.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Causes and risk factors
The process is not limited to superficial inflammation. The infection quickly spreads deeper, destroying surrounding structures. Awareness of risk factors helps people protect themselves from compression fractures and take sensible steps to maintain spinal health.

Vertebral compression fractures develop due to a variety of factors. The key causes include:
-
Traumatic impacts
Severe bruises from falls and accidents can compress the bone structures of the spine.
-
Loss of bone strength
Osteoporosis significantly weakens bones, making them vulnerable even with minimal activity.
-
Tumors
Abnormal cell growth in the spine disrupts normal bone structure, increasing the likelihood of injury.
-
Natural wear and tear of the body
With age, bones thin, losing density and elasticity, which creates the predisposition to fractures.
-
High loads
Heavy training and heavy lifting pose additional risks, especially if you have underlying musculoskeletal conditions.
Mechanical injuries and accidents
Compression fractures are often caused by severe physical trauma and accidents. Typical scenarios include falls from great heights, collisions in car accidents, or participation in dangerous sports.
A single blow of sufficient force can instantly crush a vertebral body, turning dense bone into a flattened shell. The more severe the impact or fall, the more severe the consequences for the spine.
Age-Related Changes and Osteoporosis
Age brings with it many changes, and one of them is the gradual deterioration of bone health. Elderly women after menopause and men over 65 are especially vulnerable.
According to statistics from the Russian Ministry of Health, the risk of fractures, including dangerous compression injuries of the spine, increases during this period. Even minor efforts, such as coughing, turning awkwardly, or lifting a light bag, often cause bone damage.
Classification and Types of Compression Fractures
Vertebral injuries from compression fractures are varied and depend on the mechanism of action and the condition of the bone tissue. Based on the nature of their manifestations, the following types of injury are distinguished:
- Acute fracture: occurs suddenly and unexpectedly, usually after a strong external impact, fall, or injury. This causes immediate damage to the integrity of the vertebra.
- Chronic fracture: progresses slowly and gradually, and is especially common in people with low bone mineral density, such as osteoporosis. Over time, accumulated microcracks lead to severe destruction.
По объему повреждений переломы делятся на:
- Множественные: образуются, когда страдает сразу несколько соседних позвонков. Чаще всего встречаются при тяжелых травмах, дорожно-транспортных происшествиях или сильных падениях
- Одиночные: затрагивают единственный позвонок, обычно возникают при единичных событиях — падениях или внезапных резких перегрузках. Нередко обусловлен наличием остеопоротических изменений
Также компрессионные переломы классифицируют согласно степени деформации позвонка:
- Легкая форма: высота позвонка уменьшается максимум на треть
- Среднетяжелая форма: сокращение достигает половины первоначального размера
- Тяжелая форма: тело позвонка сжимается более чем наполовину
По типу полученной травмы выделяют:
- Клиновидные переломы: примерно половина случаев относится именно к ним. Страдает центральная зона грудного отдела. Передняя сторона тела позвонка придавливается, что приводит к изменению очертаний
- Раскалывающие переломы: ломаются верхняя и нижняя пластины позвонка, сохраняя целой заднюю сторону
- Взрывные переломы: критически тяжелые типы повреждений. Перелом охватывает горизонтальную пластину и заднюю поверхность позвонка, что часто влечет за собой поражение спинного мозга и последующие тяжелые последствия (паралич конечностей)
Переломы могут затрагивать:
- Грудной отдел — лидер по числу случаев. Наибольшая доля повреждений сосредоточена в областях Th11-Th12, поскольку именно они переносят максимальные нагрузки
- Пояснично-крестцовый отдел — здесь преобладают повреждения первого поясничного позвонка (L1), сопровождающиеся сдавливанием нервных волокон
- Шейный отдел — самый редкий тип, выявляющийся главным образом у молодежи вследствие силовых воздействий на голову
Помимо указанных вариантов, существуют также случаи комбинированных повреждений, охватывающие несколько уровней позвоночника одновременно.
По наличию осложнений можно выделить:
- Неосложненные переломы — проявляются болевыми ощущениями в месте травмы, иногда иррадиацией в руки или туловище. Может протекать скрыто, бессимптомно
- Осложненные переломы: обломки кости проникают в нервные структуры, усугубляя симптоматику. Наблюдается выраженный болевой синдром, а также неврологическая симптоматика (онемение, слабость мышц, парезы)
Терапия и стратегия наблюдения зависят от конкретного вида перелома, его масштабов и природы повреждения.
Symptoms and clinical manifestations
The consequences of a spinal compression fracture vary depending on the location of the injury and the degree of vertebral destruction. The main symptom is severe pain at the point of injury, radiating to the arm or leg. The nature of the symptoms depends on the location of the fracture:
- Thoracic spine: difficulty taking a deep breath, chest and heart pain, tingling or numbness in the extremities, problems with urination and sexual function.
- Lumbar spine: girdle-like pain radiating to the buttocks and legs, difficulty walking, possible paralysis of the lower body, inability to raise a limb.
- Cervical spine: severe neck pain radiating to the head, shoulders, and arms, increased pain when turning the neck, dizziness, tinnitus, discomfort when swallowing and breathing.
Spinal fractures are often accompanied by asymmetry. Fever, which is characterized by elevated body temperature, may also occur.

Pain and limited mobility
A characteristic sign of injury is pain when palpating the affected area. This pain may appear suddenly or increase gradually, becoming unbearable. A characteristic feature of this type of pain is that it intensifies when attempting to move, turn, or bend.
Another important symptom of a spinal fracture is pain that begins not only at the fracture site itself, but also in the lower abdomen, legs, and arm. The reason is simple: the nerves running along the spine are damaged, and this affects the condition of other organs.
The main characteristic of pain with this type of fracture is its persistence and depth. It is difficult to relieve with conventional medications, so it is important to see a doctor immediately. Compression injuries can also cause redness and swelling of the skin, as well as a significant decrease in mobility. The injury often triggers a headache.
Neurological manifestations
Complicated fractures affecting nerve endings near the spine are particularly worrisome. These can cause alarming neurological signs:
- Movement disorders in the arms and legs
- Loss of sensation in certain areas of the body
- Bladder and genital dysfunction (urinary and fecal incontinence, sexual dysfunction)
- Nausea
- Dizziness
General weakness and fatigue are often observed following a spinal injury.
Diagnosis of compression fracture
X-ray examination
The first step in diagnosing a spinal compression injury is a standard radiograph. The patient's spine is imaged in two mutually perpendicular planes—lateral and anterior projections. This is a basic examination that provides an initial picture of the injury.
Although an X-ray cannot show all the details, it provides important information confirming the fracture and allowing a rough assessment of the extent of the injury.
The doctor can see the general outline of the vertebrae, noting their deformation, possible displacement and loss of height, as well as indirect signs of instability of the spinal segments. A preliminary diagnosis established by X-ray results is necessary to determine further examination tactics.
MRI and CT scan
These technologies provide a comprehensive view of the spine, from the bones to the soft tissues and vascular system. MRI is particularly effective at demonstrating the condition of the soft tissues and spinal cord, helping to detect potential problems with intervertebral discs, hematomas, and inflammatory processes.
CT, in turn, is indispensable for assessing bone condition, fractures, and degenerative changes, and also helps plan surgical interventions and further treatment. These diagnostic methods complement each other, providing the physician with the most complete picture of what is happening in the patient's body and enabling the development of an effective treatment strategy.
Treatment of compression fractures
The approach to treating a spinal compression injury is always individualized and based on the patient's unique characteristics and the specific circumstances of the injury. A personalized treatment program and consistent adherence to medical recommendations can minimize the negative consequences of the injury and help patients return to an active lifestyle as quickly as possible.
Conservative treatment
For stable fractures without complications, conservative treatment is preferred. The patient requires:
- Long-term rest. This period varies from a couple of weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the injury.
- Avoiding axial load on the spine.
- Wearing a rigid orthopedic belt or a special apparatus to immobilize the spine and facilitate fusion.
Additionally, the doctor will prescribe medication to relieve pain and promote rapid recovery. The most commonly used medications are:
- Analgesics for acute pain relief
- Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce inflammation and swelling
- Medications containing vitamins and minerals that support bone tissue
- Medications that stimulate cartilage regeneration
Physical exercise is necessary to maintain muscle and joint function. Prolonged rest in bed without movement can lead to muscle atrophy, blood clots, bedsores, and other negative effects.
Training begins with breathing exercises and lying positions, gradually expanding the range of loads. Therapeutic exercises are performed under the supervision of medical staff.
Physical therapy is introduced approximately six weeks after the injury. A wide range of procedures are used:
- Electro-stimulation and electrophoresis to stimulate blood circulation and relax tense muscles
- Shock wave therapy to enhance tissue regeneration
- Hydrotherapy and heat treatments to improve blood flow and promote relaxation
- Reflexology and laser therapy to stimulate metabolic processes
- Acupuncture for comprehensive health improvement
The number of physiotherapy sessions is usually limited to ten to twelve. Another important component of rehabilitation is massage. Properly selected techniques help restore mobility, improve blood circulation, and reduce the risk of muscle wasting. A course typically consists of ten sessions, but can be repeated later if necessary.
Surgical treatment
Surgery is recommended if conservative treatment methods fail to produce the desired result, as well as in situations involving:
- Neurological disorders manifested by symptoms of numbness, weakness, and pain in the extremities
- Signs of compression of the spinal cord or its roots, leading to loss of sensation and functional ability
- Spinal instability threatening further damage
The main goal of surgery is to release pinched nerve fibers and stabilize injured spinal fragments. Modern medical practice prefers gentle, minimally invasive techniques, but any surgery in the elderly carries an increased risk due to age-related diseases.
Methods: vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty
Some of the most popular surgical procedures are vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Vertebroplasty involves injecting a special compound called polymethyl methacrylate into the vertebral body. This rapidly hardening material strengthens the vertebra, restores its shape, and relieves pain. Vertebroplasty is most effective if no more than six months have passed since the injury. Contraindications to the procedure include spinal infections, poor blood clotting, allergic reactions to the components of the solution, and displacement of bone fragments deeper into the spinal canal.
Kyphoplasty is similar to vertebroplasty, but before cement is added, a special balloon is inserted to expand the space in the vertebral body. The balloon is filled with a contrast agent, allowing the position of the vertebra to be monitored using X-rays. After the balloon is removed, the empty space is filled with cement. Kyphoplasty allows for straightening the spine and restoring 50-70% of lost height.
Prevention and recommendations
To protect yourself from the risk of a spinal compression fracture, focus on injury prevention and treatment of bone and vascular diseases. Regular exercise to strengthen the deep back muscles will provide reliable support for the spine.
It's important to avoid excess weight—this will prevent unnecessary pressure on the back. Proper nutrition is also crucial. It provides the body with essential nutrients. Your diet should be lower in fatty foods and sugar, and higher in vegetables, fruits, and calcium-rich foods.

Questions and Answers (FAQ)
What are the first steps to take if you suspect a fracture?
Contact a traumatologist or surgeon immediately. Before your appointment, try to limit movement and physical activity to avoid worsening the condition. The doctor will order an examination and confirm the diagnosis with an X-ray, MRI, or other diagnostic procedures.
Is it possible to treat a compression fracture without surgery?
Yes, many fractures can be successfully treated conservatively. Rest, special braces, pain medications, and physical therapy are typically prescribed. Surgery is only necessary in cases of severe vertebral damage or nervous system dysfunction.
How quickly can I return to sports after treatment?
Return to sports is individual and depends on the severity of the injury, the chosen treatment method, and the body's response to therapy. The minimum recovery period is approximately three to six months. Before resuming training, be sure to consult with a doctor.
What complications can arise if treatment is not given in a timely manner?
Neglecting proper attention to an injury can lead to a multitude of unpleasant consequences: chronic pain, poor posture, decreased quality of life, and disruption of internal organs and the musculoskeletal system. The longer a person delays seeing a specialist, the more difficult and time-consuming the recovery process will be.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price














































































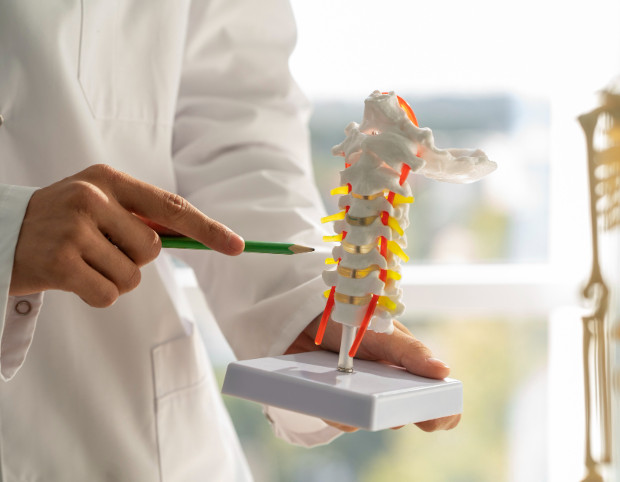
Definition and General Information
A compression fracture occurs when severe downward pressure is applied to the spine. This injury is more common in people with increased bone fragility caused by calcium and vitamin deficiencies, such as osteoporosis. Bone structure weakens, and a vertebra can be fractured even with a minor fall or an awkward movement.
This type of injury is quite likely to occur in anyone exposed to significant stress, such as athletes, road accident victims, and construction workers. The damaged vertebra changes shape and becomes compressed, leading to spinal curvature and possible nervous system disorders.
A compression fracture is not only a physical fracture of the bone but also a serious health threat, leading to changes in the spine and potential consequences for the nervous system.