Endovascular Surgery Techniques
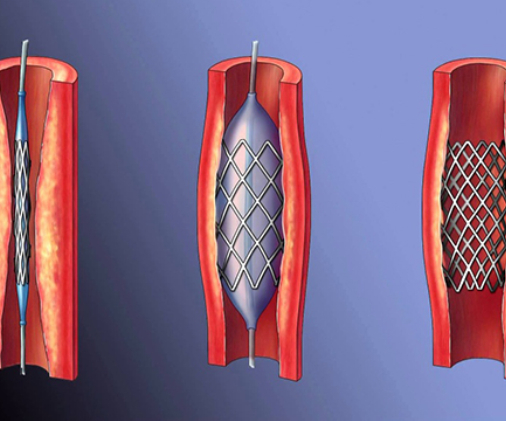
Balloon angioplasty and stenting. The narrowed vessel is expanded from the inside with a balloon catheter, after the expansion of the vessel, a stent is installed in it - a special design that looks like a spring from a ballpoint pen, which prevents re-narrowing of the lumen and detachment of the inner shell of the vessel. This is the most common technique of endovascular surgery, used both for the treatment of lesions of the arteries of the heart, and for the treatment of lesions of the peripheral arteries. Balloon catheters and stents come in different diameters and lengths, as well as with different physical properties, depending on the parameters of the vessel for which they are intended. Stents are made of various materials - high-tech polymers and metal alloys, they can have a special drug coating that prevents reverse vasoconstriction (restenosis).
Embolization. Inside the vessel, spherical emboli or spirals closing the lumen of the vessel are inserted. The diameter of the injected particles is fractions of a millimeter, and is usually measured in nanometers. Spirals also come in different thicknesses and lengths, and have different coatings necessary to completely stop the blood flow in the vessel. This technique is applicable in the treatment of tumors (including uterine fibroids), varicocele, internal bleeding. Also, the particles can be a carrier of a chemotherapy drug that is used in the treatment of malignant tumors.
Endoprosthetics. Installation of a stent-graft inside the affected vessel. A stent graft is a stent covered with an artificial or natural (from an animal vessel) sheath. This method of treatment has shown high efficiency in the fight against vascular aneurysms - for example, an aneurysm of the abdominal aorta, or an aneurysm of the splenic artery, and is also used in emergency care for ruptured arteries.
Mechanical catheter thrombectomy and thrombolysis - methods of physical removal of blood clots from the lumen of the vessel using special catheters or dissolution of blood clots using enzymes (thrombolytics). Unlike open vascular surgery, the methods are less invasive, have a much lower number of complications, and are more effective, especially in complicated cases (for example, with shunt thrombosis, when access to them is difficult due to cicatricial deformity).
Catheter atherectomy is a method of removing atherosclerotic plaques from arteries using special catheters. It is used for endovascular interventions on the arteries of the lower extremities, which, in combination with other methods of restoring the lumen of the vessels, makes it possible to obtain the most long-term result of the intervention.
Carboxangiography is a technology that involves the introduction of carbon dioxide into a vessel using special equipment instead of the usual iodine-containing contrast agent for diagnostics or surgery. It is used in patients with significant impairment of kidney function or with an allergic reaction to iodine-containing contrast agent.
Before endovascular interventions, the patient must undergo a preoperative examination.
Benefits of Endovascular Surgery at K+31 Clinic
- Advanced diagnostic and therapeutic options - endovascular surgery techniques allow interventions on vessels of very small diameter (2-3 mm), which are often inaccessible to open surgery, as well as restoring the lumen of their own vessels.
- Low invasiveness of the operation - there is no need to make large skin incisions, there are no scars after the operation, the likelihood of infectious complications (suppuration of the wound) is minimal.
- Short postoperative period - discharge from the hospital is possible the next day after the operation.
- Specialists-experts - at the K + 31 clinic, endovascular operations are performed by specialists who are highly qualified in cardiovascular surgery, who are experts in every field of minimally invasive endovascular interventions.
- Latest generation professional European and American equipment


How is an abdominal aortic replacement performed?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.




























Endovascular surgery is a section of innovative methods for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, which consists in a therapeutic effect from the inside of the affected vessel. Such interventions are performed under local anesthesia in an X-ray operating room, but without the need to turn off consciousness and transfer to artificial ventilation.
The general principle of the operation is as follows: a puncture is made in the vessel through the skin in the groin or wrist area, through which a vascular port with a valve is installed inside the vessel. Conductors, catheters, balloons, stents, coils, occluders and other instruments are inserted into the vessel through the port.
After the operation, the patient recovers very quickly without the need for a long stay in the hospital and in most situations can be discharged the next day after the intervention. During all procedures, heart rate, blood pressure, blood oxygen saturation are necessarily monitored.