Surgical dentistry in Moscow

specialists

equipment

treatment
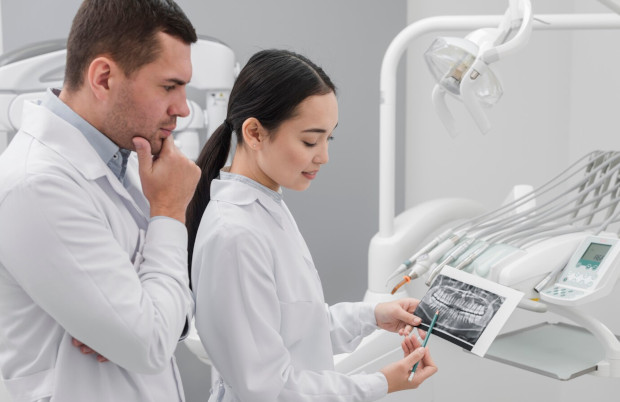

Some dental problems require surgery. In particular, surgical intervention is necessary in the case of:
- Damage to the jaw bone
- Inflammation of the soft tissues of the mouth
- Congenital defects of the face or jaw
- Wisdom teeth that are not growing correctly
- Tumors in the oral cavity (benign, malignant)
Surgical treatment is considered when it is impossible to save the tooth. It is also carried out if traditional means fail to prevent the spread of infection.
Surgical dental services
The K+31 Clinic offers a wide range of surgical dental services. Experienced dental surgeons perform various procedures, ensuring the comfort and safety of every patient.
Tooth extraction
The surgeons at the K+31 clinic perform gentle tooth extractions of any complexity. Simple extractions are suitable for loose teeth, while complex extractions are suitable for firmly seated roots. Particular attention is paid to wisdom teeth, as their anatomy often poses challenges. Our specialists carefully extract the tooth, minimizing pain and accelerating wound healing.
Dental implantation
We offer progressive approaches to dental implantation, enabling high-quality restoration of the dentition. Single-stage implantation involves inserting the implant immediately after tooth extraction, minimizing treatment time. The traditional method involves a step-by-step approach: first, implant placement, then prosthetics. We use high-quality materials and modern technologies, ensuring a reliable and long-lasting solution.
Gum and soft tissue plastic surgery
At the K+31 clinic, we perform gum plastic surgery, which improves the appearance of your smile and corrects defects of the oral mucosa. These procedures are beneficial not only for beauty but also for your health: correcting defects prevents inflammation and decay in adjacent teeth.
Bone tissue surgery
Sinus lift is an increase in the bone volume of the upper jaw for subsequent implant placement. Bone grafting addresses the issue of insufficient bone in the patient's own mouth, providing a reliable foundation for future dentures. Each case is individual, and our specialists select the appropriate treatment method based on the individual patient's wishes and needs.
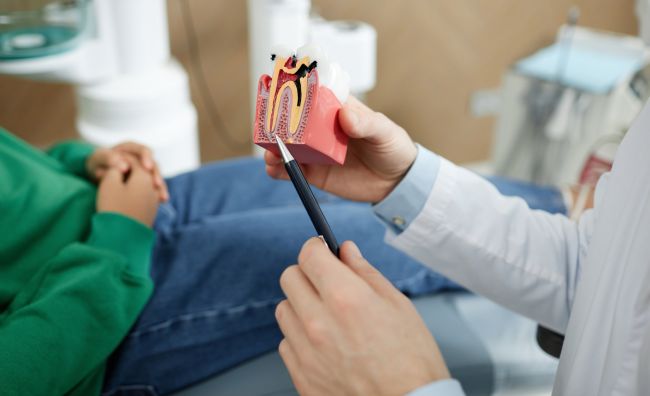
There are several restrictions on performing medical surgical procedures. Here they are:
- Heart and vascular diseases
- Acute diseases of the liver, kidneys, spleen, pancreas (viral hepatitis, glomerulonephritis, acute pancreatitis)
- Hemorrhagic disorders (acute leukemia, agranulocytosis)
- Acute infectious diseases (flu, acute respiratory viral infections, erysipelatous inflammation, pneumonia)
- Some diseases of the central nervous system (acute cerebrovascular accident, meningitis, encephalitis)
- Schizophrenia, bipolar affective disorder, epilepsy and other mental illnesses in the acute stage
After the condition improves, the problem tooth can be removed.
General information about surgical dentistry
Advantages of surgical dentistry "K+31"
During surgical interventions, the specialists of the K+31 clinic use gentle and effective methods. Our other advantages:
- The clinic team includes doctors with extensive professional experience. They take on even the most complex problems
- We use advanced equipment (3D tomographs and microscopic systems are used for precise visualization of the maxillofacial area) and materials (biocompatible implantation systems and new generation anesthetics)
- The clinic has impeccable reviews on all sites
To make an appointment, use the application form. Check the prices for surgical dentistry and other services at the K+31 center (Moscow) on our website and by phone.
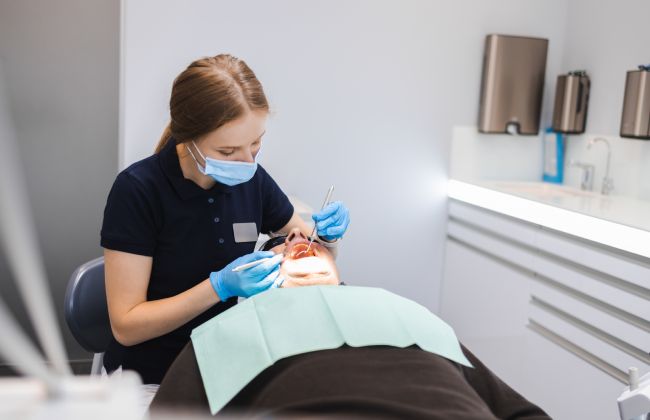
FAQ
How painful are the procedures?
How long does recovery take?
Is it possible to have a tooth extracted and an implant placed in one day?
How to choose a good dental surgeon?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services
Other Services







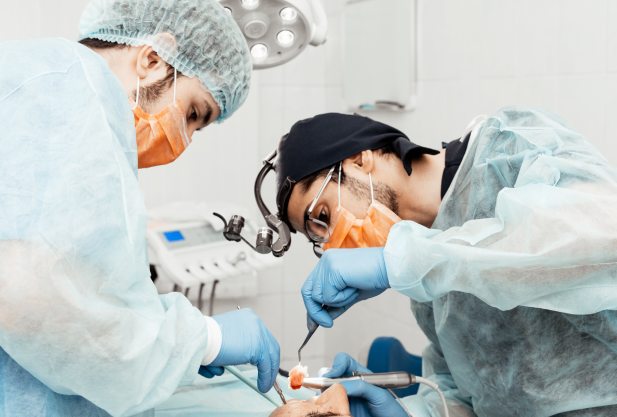









































































About the service
The specialists of the Dentistry Department of the Clinic +31 use the latest treatment methods recognized by leading dentists in the USA and Europe.
The main tasks of surgical dentistry:
The surgical dentistry of the Clinic K +31 aims to ensure the health and impeccable aesthetic appearance of your smile with maximum preservation of teeth. The work of dental surgeons is closely related to the treatment measures carried out by therapists, periodontists and orthopedists. The main principles of joint work of a group of dentists are based on the occlusal concept.