Femoral Neck Fracture Treatment
A femoral neck fracture is considered one of the most severe skeletal injuries, especially in the elderly. This injury is associated with a high risk of adverse consequences due to the specific blood supply to this area and the complexities of its anatomy.
Treatment approaches range from conservative methods to surgical interventions, including fixation of fragments and placement of an endoprosthesis. The choice of method is determined by the nature of the fracture, age, and overall health of the patient. Timely detection of the injury and subsequent rehabilitation are crucial.

specialists
equipment
treatment
Causes and risk factors
Age factors
Older adults are significantly more susceptible to hip fractures than younger patients. This vulnerability is explained by a complex of age-related changes affecting the skeletal system and the entire body.
The main reasons for the increased risk:
- Development of osteoporosis - by age 70, bone loss reaches 30%
- Decreased muscle tone and impaired coordination
- Deterioration of vision and cognitive function
- Decreased bone reparative capacity
- Impaired calcium metabolism and bone mineralization
A combination of several factors is especially dangerous. For example, osteoporosis combined with poor balance increases the likelihood of severe fractures from falls. Age-related changes in bone blood supply further complicate the situation, slowing natural recovery processes.
From a medical perspective, age 65 and older is considered a critical period. During this period, bone density declines most rapidly, and the body's compensatory abilities are significantly reduced. This creates ideal conditions for severe fractures to occur, even with minor injuries.
Injuries and falls
Femoral neck injuries are diagnosed in patients of various age categories. Common causes often result from falls.
The most dangerous mechanisms of injury are the following:
- Side falls with a direct blow to the hip joint
- Falls with support on a straight leg, accompanied by a twist of the torso
- Slipping on slippery surfaces
In severe osteoporosis, a fracture can occur even without significant external impact.
In such extreme cases, femur damage sometimes occurs in the following situations:
- A sharp turn of the body
- An unsuccessful squat
- Normal walking on an uneven surface
A characteristic feature of such injuries is the frequent absence of severe pain in the first few hours. This leads to delayed medical attention.
Caution! In older patients, a fracture can occur with a simple fall from a standing position. This requires a mandatory examination to rule out femoral neck damage.
Classification of femoral neck fractures
It is necessary to systematize different types of bone injuries in order to predict the outcome of healing, assess the level of trauma, the need for surgical treatment and the duration of recovery.
The type of fracture has a direct impact on the choice of treatment. Intra-articular injuries often require complex surgery due to impaired trophism of the femoral head. With extra-articular variants, non-surgical therapy is possible.
There are several principles of classification:
-
By location of damage
Subcapital (closer to the articular head), transcervical (in the central part of the neck), basicervical (on the border with the shaft of the femur).
-
By the degree of displacement of bone fragments
Impacted (fragments are partially fixed), with displacement (grades Garden I–IV).
-
By orientation of the fracture line
Vertical, transverse, oblique.
-
By location relative to the joint capsule
Intra-articular, extra-articular.
The main cause of felon is infection entering the soft tissues of the finger through damaged skin. Local inflammation develops at the site of the cut or injection, which quickly spreads inward.
Factors that trigger the development of the disease include:
- Microtrauma to the skin (cuts, splinters, injections)
- Poor hand hygiene
- Nail biting or hangnail picking
- Infection during a manicure
- Diabetes and weakened immunity
- Chronic skin diseases (e.g., eczema)
- Prolonged contact with chemicals without gloves
Most often, the lesion forms near the nail fold, in the cuticle area, or under the nail plate. The main pathogens are staphylococci and streptococci, which actively multiply when the skin's protective functions are weakened.
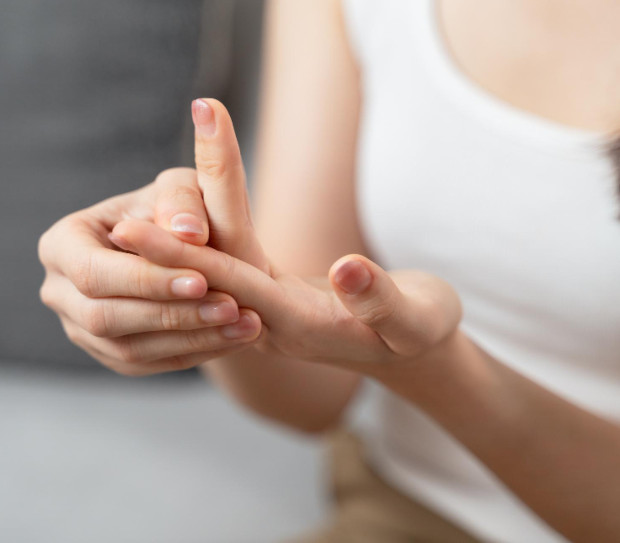

Main risk factors
The development of felon is often associated with repeated microtrauma and a weakened local immune system.
Those most at risk are:
- People with weakened immune systems
- People with diabetes
- Workers who perform manual labor
- Children who frequently bite their nails and overlook minor cuts
The more frequently an arm or leg is injured, the higher the risk of infection. Certain health conditions and lifestyle choices increase vulnerability to infection.
Diagnostics
To accurately determine the presence of a femoral neck fracture, an X-ray is first prescribed. This method allows you to quickly identify the displacement, direction of the fracture line and the general condition of the bone tissue. However, in some cases, a regular X-ray does not give a complete picture. This is especially true for intra-articular cracks and minor injuries. In such situations, a CT or MRI scan is additionally performed, which help to detail the condition of the cartilage, blood vessels and soft tissues.
The patient receives the results within 1-2 days. The doctor's conclusion not only confirms the fracture but also determines the treatment tactics. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the higher the chance of avoiding complications.
Treatment methods
Conservative treatment
For uncomplicated neck injuries. Conservative treatment is also possible with minimal displacement of femoral fragments.
This approach is chosen in the following cases:
- stable fracture without displacement in young patients
- medical contraindications to surgery (severe comorbidities)
- patient refusal of surgery
- extremely high surgical mortality in the elderly
For older people, non-surgical treatment remains risky: prolonged immobilization threatens pneumonia, bedsores, and thrombosis. However, if surgery is not possible, even passive bed rest can save lives.
The average duration of therapy is 8 to 16 weeks. Success depends on physiological parameters, age, and disciplined care. Complete recovery from a hip fracture without surgery is rare; more often, limited mobility and the need for care remain.
Surgical treatment
In unstable injuries, with displaced bone fragments and severe pain, surgery is the only way to maintain mobility and avoid serious complications. This is especially true for the elderly, who have virtually no chance of recovery without intervention.
Osteosynthesis
This is a procedure in which bone fragments are joined using metal structures to restore the anatomical shape and accelerate healing. This method is most often used for impacted fractures in active young individuals, when preservation of the native joint is possible. During surgery, screws, pins, or plates are inserted directly into the fracture site.
The most common fixators for femoral neck injuries are:
- Cannulated screws (inserted under X-ray guidance)
- DHS systems (dynamic femoral plate)
- Three-blade nails and locking pins
This surgical treatment is indicated for stable injuries without significant displacement. Its main advantage is the preservation of the natural joint and minimal tissue intervention.
However, osteosynthesis also has risks. Complications include failure to unite, recurrent fracture, femoral head necrosis, or loosening of the structure. It is especially important to strictly follow the recommendations during the rehabilitation period to avoid complications.
Endoprosthetics
If a femoral neck fracture is severely displaced or occurs in an elderly patient with low bone density, endoprosthetics are preferred. This is a complete replacement of the damaged joint with an artificial one, avoiding a long healing process and reducing the risk of complications.
There are two types of endoprosthetics: unipolar (only the upper part of the femur is replaced) and total (the entire joint is replaced). The difference lies in the extent of the intervention and the service life of the implant. Depending on the patient's age and bone condition, the doctor selects the most appropriate option.
Surgery for femoral neck injury with endoprosthetics is performed under anesthesia and requires rehabilitation. The surgery itself lasts approximately 1.5–2 hours. The average cost depends on the clinic's level, materials, and scope of services. The price typically includes consultations, the implant, hospital stay, and postoperative follow-up.
Modern prostheses last for 15–25 years. To extend their lifespan, it's important to have regular check-ups with a specialist, avoid overloading the joint, and follow recommendations for preventing recurrent injuries.
First aid, complications, rehabilitation
Prognosis and Prevention
In older people, the prognosis after a hip fracture depends on the time of initiation of therapy and the quality of rehabilitation. With early treatment and adequate treatment, partial or complete restoration of mobility is possible. However, with age, the risk of complications, including loss of independence, increases.
It is impossible to completely eliminate the possibility of injury, but competent prevention can significantly reduce the risks. It is important not only to maintain bone health, but also to create a safe living environment.
The most effective measures:
- Regular moderate physical activity loads
- A balanced diet with sufficient calcium and vitamin D
- Control of chronic diseases
- Correction of vision and coordination disorders
- Non-slip surfaces in the bathroom and hallway
- Adequate lighting in living spaces
By following these recommendations, even in old age, you can remain active. Also, avoid serious consequences.

Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to recover from a hip fracture?
If treatment is started promptly and rehabilitation is carried out according to all standards, the recovery period can range from 3 to 12 months. The duration depends on the patient's age, the presence of chronic diseases, and their overall physical condition.
Is surgery necessary for a hip fracture?
In most cases, surgery is unavoidable. Osteosynthesis or endoprosthetics are often used to restore hip mobility, especially in older adults. The choice of technique depends on the nature of the fracture and the individual patient's characteristics.
Is it possible to do without surgery?
If surgery is contraindicated, for example due to severe comorbidities or the risk of anesthesia, conservative therapy may be an option. However, it's important to keep in mind that this approach can lead to complications, decreased mobility, and a deterioration in quality of life.
How do you prepare for surgery?
Preoperative preparation includes a number of mandatory procedures: necessary tests, instrumental examinations, and consultations with specialists (including a physician, cardiologist, and anesthesiologist). Treatment of underlying conditions is also performed to minimize potential risks during surgery and in the postoperative period.
What complications are possible after fracture treatment?
Even if all recommendations are followed, adverse effects are possible: blood clots, surgical wound infection, and bone fusion problems. These risks are significantly reduced with constant medical monitoring, proper rehabilitation, and adherence to the regimen after discharge from the hospital.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price







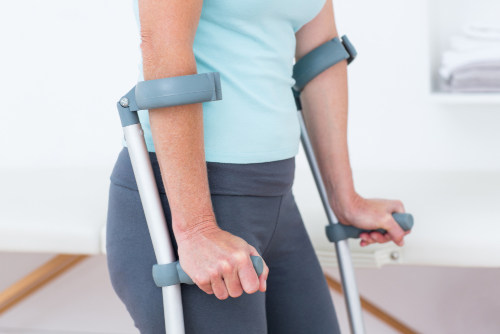
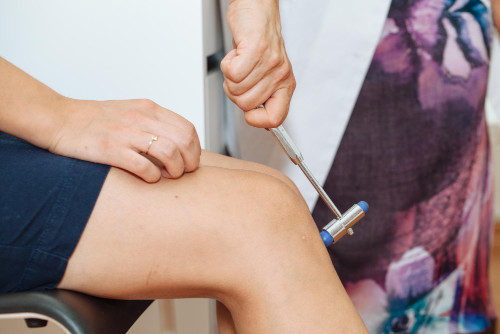


































































General information about hip fractures
The femoral neck is a narrow fragment connecting the head and central portion of the femur. This anatomical structure is poorly vascularized, increasing the risk of ischemia during injury.
A fracture affects the following structures:
Modern treatment methods take these factors into account, offering an individualized approach to each case of femoral injury. However, problems may arise during treatment.
Effective medical care for femoral neck fractures faces a number of objective challenges:
When developing a treatment plan, careful selection of the optimal treatment method—whether conservative approaches or surgical intervention—is crucial, as this choice determines the dynamics of rehabilitation, the degree of preservation of joint mobility, and the long-term prospects for restoring the patient's normal functioning.