Treatment of tonsillitis

specialists
equipment
treatment
Functions of the tonsils
The palatine tonsils (or glands) are an important organ of the immune system. They are located at the entrance to the respiratory tract and are the first to come into contact with inhaled microorganisms. Their main function is to recognize pathogens and produce protective antibodies. They act as a barrier, preventing infection from penetrating further into the body. In a healthy state, the tonsils actively contribute to the immune system. With the development of chronic tonsillitis, their protective function is reduced, and they themselves become a source of constant infection.
Why does inflammation of the tonsils develop?
The main causes of chronic tonsillitis stem from the body's inability to completely eliminate the infection after the acute phase. Pathogenic microorganisms, most often streptococci and staphylococci, persist deep within the tonsils, in their tortuous channels (lacunae). There, they form biofilms – special communities protected from the effects of antibiotics and immune cells.
A weakened immune system creates favorable conditions for the existence of such a hidden lesion. The immune system fails to adequately respond to pathogens, allowing them to maintain a sluggish inflammatory process. The very anatomical structure of the tonsils, with deep and narrow lacunae, hinders their natural self-cleansing, contributing to stagnation and chronic inflammation.
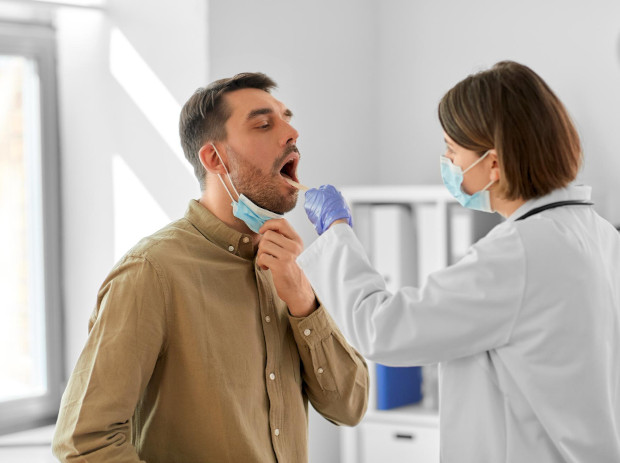
Risk factors
There are a number of circumstances that significantly increase the likelihood of developing the disease. The main causes of chronic tonsillitis include frequent acute respiratory infections and sore throats, especially if treatment is incomplete or untimely. The presence of other foci of infection in the body also maintains a constant infectious load, including:
- Caries
- Sinusitis
- Adenoiditis
Difficulty breathing through the nose, caused by a deviated septum or allergic rhinitis, forces a person to breathe through the mouth, which dries out the pharyngeal mucosa and reduces its protective properties. A general weakening of the immune system due to stress, poor nutrition, or unhealthy habits is also a significant risk factor.
Forms of tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of one or more tonsils caused by an infection. It is common during the cold season – winter and spring.
Depending on the course of the disease, tonsillitis is classified as acute and chronic.
Acute Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is an infectious disease characterized by inflammation of the tonsils. It is most often caused by staphylococci and streptococci.
Previously, it was believed that bacterial tonsillitis could only develop in people over 3 years of age, but now the disease is becoming more common and can affect even very young children.
Chronic Tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term inflammation of the tonsils with the constant presence of bacteria. It usually develops alongside a sore throat, but can also occur without it. The main danger is the persistent presence of infection, which negatively impacts the overall health of the body and increases the risk of various diseases.

Reasons
Frequent acute viral respiratory infections, sore throats, oral problems (caries, periodontitis), and many other conditions can lead to the development of tonsillitis. People with a deviated nasal septum or infectious diseases of adjacent organs (sinusitis, adenoids) are also predisposed to this disease.
In Children
Tonsillitis is one of the most common childhood diseases. It most often affects children over 5 years of age and young adults up to 25 years of age. Those at risk include those with immunodeficiency and a genetic predisposition. The illness typically lasts about 7 days.
In Adults
Adults tolerate tonsillitis much better, but this doesn't mean it requires less attention. It's important to treat a sore throat promptly and effectively to prevent tonsillitis from progressing to a decompressed stage, which can be much more problematic.
During pregnancy
It's especially important not to self-medicate. If you notice symptoms, make an appointment with your doctor immediately. When choosing a treatment method, avoid procedures and medications that could harm the baby. Tonsillitis in pregnant women is very dangerous and can lead to a host of complications, such as toxicosis and kidney disease (glomerulonephritis).

Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
The symptoms of chronic tonsillitis differ significantly from those of acute tonsillitis. Clinical signs are often vague and fluctuating. Patients are bothered not by acute pain, but by a constant sensation of irritation, scratchiness, or a lump in the throat. The hallmark of the disease is the formation of caseous plugs in the lacunae of the tonsils—dense, whitish masses that cause bad breath. A persistent low-grade fever (temperature 37.0–37.5°C) is often observed.
The disease also manifests itself with signs of general intoxication: constant malaise, decreased performance, and fatigue. Examination may reveal enlarged and tender submandibular lymph nodes.
Pathogenesis of Chronic Tonsillitis
The development of chronic tonsillitis is associated with the persistent loss of the palatine tonsils' protective capacity. In a healthy state, they act as a barrier to infection, but when the infection becomes chronic, they become a reservoir. Pathogenic bacteria colonize deep lacunae, where they form biofilms resistant to immune attacks. Their waste products and toxins constantly enter the bloodstream, maintaining general intoxication. The immune system, under constant antigen stress, can malfunction, triggering autoimmune reactions. Thus, the tonsils transform from a protective organ into a source of threat to the entire body.

Symptoms of the disease
- Pain in the throat
- Bad breath
- Enlarged tonsils
- Swelling in the nasopharynx
- Difficulty swallowing
- In addition, swollen lymph nodes and fever are possible.
Types of tonsillitis
Catarrhal
Catarrhal tonsillitis develops very quickly, beginning with a burning sensation in the throat, dryness, and then progressing to distinct pain. The fever ranges between 37 and 38 degrees Celsius. It usually lasts up to a week, then the symptoms disappear.
Follicular
Follicular tonsillitis is an infectious disease accompanied by severe intoxication. It is characterized by a high fever, severe pain when swallowing, weakness, and fever. The tonsils become significantly enlarged and covered with white spots. Viral tonsillitis in children can be accompanied by nausea, diarrhea, and confusion.
Lacunar
Similar to the previous variant, but more complex. A significant amount of white plaque appears on the inflamed tonsils.
Ulcerous-membranous
This type of tonsillitis is caused by the interaction of a spirochete and a fusiform rod found in the mouth. It is characterized by the death of the tonsil surface, followed by the development of an ulcer. A foul odor, a sensation of a foreign body in the throat, and increased salivation occur. Body temperature remains normal.
Necrotic
The causes and symptoms are the same as for the previous form. Typically, only one tonsil is affected, but bilateral infections are also possible. Body temperature does not rise. This type of tonsillitis is not contagious, but it can be epidemiological.
Phlegmonous
A very rare form of tonsillitis characterized by purulent melting of the tonsils. A unilateral form is common, with the tonsil becoming greatly enlarged and painful. Swallowing becomes very difficult, the temperature rises to 40 degrees Celsius, and general intoxication is observed.
General information
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Treatment strategies for chronic tonsillitis are determined by a physician based on the severity of the disease and the presence of complications. At our clinic, tonsillitis is treated using modern techniques. Conservative measures are the basis of therapy for compensated tonsillitis. These measures aim to eliminate the source of infection, remove pathological material from the lacunae, and boost local immunity. These measures include tonsil irrigation courses, various physical therapy procedures (such as ultraviolet irradiation), and medication.
Conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Conservative treatment for chronic tonsillitis includes a course of rinsing the palatine tonsil lacunae with antiseptic solutions. This allows for the mechanical removal of caseous plugs and pus, reducing the infectious load. Physiotherapy methods, such as quartz tube therapy or laser therapy, which have bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effects, are additionally prescribed. Antiseptic sprays and rinses are also applied topically.
Pregnancy and chronic tonsillitis
An exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis during pregnancy poses a risk to both the mother and the fetus. The infection can cause toxicosis or intrauterine infection. Treatment is carried out with extreme caution. Preference is given to local procedures, such as rinsing the lacunae and rinsing with approved antiseptics. The use of systemic antibiotics is possible only under strict indications and under the supervision of a physician.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment of chronic tonsillitis (tonsillectomy) is indicated:
- In decompensated cases of the disease
- Frequent sore throats
- Development of complications
- Ineffectiveness of conservative therapy
Tonsil removal can be performed using both the classical method and modern technologies: coblation (cold plasma surgery) or radiofrequency ablation, which reduces blood loss and accelerates healing.
Contraindications to tonsillectomy
Surgical treatment of chronic tonsillitis has a number of contraindications. Absolute contraindications include:
- Severe blood diseases with clotting disorders (hemophilia)
- Decompensated heart or kidney failure
- Active tuberculosis
- Oncological diseases
Any acute infectious process in the body serves as a temporary contraindication.
Treatment with folk remedies
Home remedies can only serve as a supplement to the main course of treatment for chronic tonsillitis prescribed by a doctor. Gargling with herbal infusions (chamomile, sage) has a moderate antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. However, they are unable to remove biofilms and purulent plugs from deep within the lacunae. Self-medication without specialist supervision can lead to disease progression and complications.
Forecast. Prevention
With timely and adequate treatment of chronic tonsillitis, the prognosis is favorable. Conservative therapy can achieve long-term remission, while surgical treatment can completely eliminate the source of infection. Prevention includes:
- Hardening
- Remediation of carious teeth
- Timely treatment of diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses
- Maintaining overall immunity through a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle
Bibliography
- Palchun V.T., Magomedov M.M., Luchikhin L.A. Otorhinolaryngology: textbook for universities. – 3rd ed., rev. and additional – M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2020. – 656 p.
- Kryukov A.I., Turovsky A.B. Chronic tonsillitis: modern concepts // Bulletin of Otorhinolaryngology. – 2017. – No. 4. – pp. 4-9.
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Services

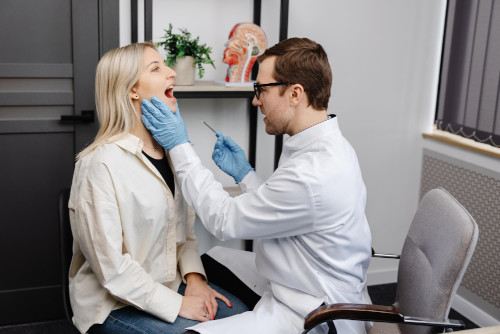


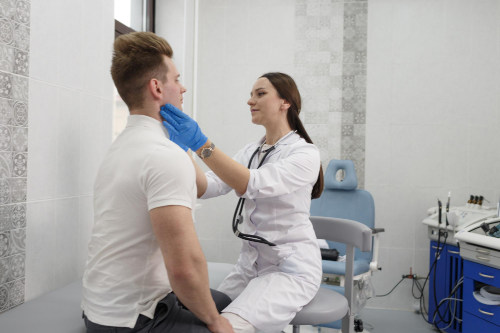



































Definition of the disease. Causes of the disease
Chronic tonsillitis is a persistent inflammation of the tonsils, characterized by failure to fully recover from an acute infection. Instead of a protective barrier, the tonsils become a constant reservoir of pathogens, exerting a toxic effect on the body. Timely diagnosis at our specialized tonsillitis clinic allows us to halt the pathological process and avoid serious consequences.
The main causes of chronic tonsillitis are multifactorial. Often, the trigger is incompletely treated sore throats, after which pathogenic microflora, particularly streptococci and staphylococci, colonize the deep, tortuous channels of the tonsils (lacunae). There, the bacteria form biofilms that protect them from the immune system. The development of the disease is facilitated by weakened immune defenses, the presence of foci of infection in the oral cavity and nasopharynx (caries, sinusitis), and anatomical features that impede drainage of the lacunae. In some cases, the pathology can develop without prior acute episodes, against the background of a general decrease in the body's resistance.