Endoscopy of ENT organs

specialists
equipment
treatment
Types of endoscopes
Endoscopy is recommended for children from 2 years of age. Before starting the procedure, the doctor performs anesthesia.
Flexible
Tough
Goals of endoscopic examination of ENT organs
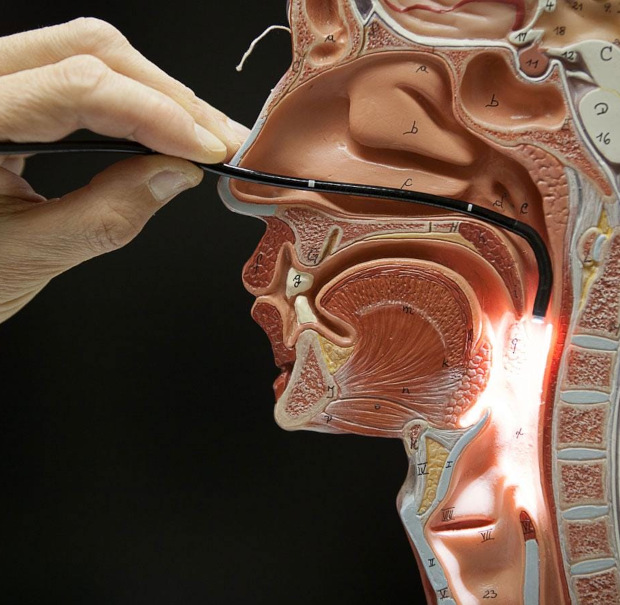
Endoscopy of ENT organs is an indispensable tool in the diagnosis of various diseases. This method allows you to:
- Detect nasal polyps, providing data on their size, location and features
- Find out the causes of constant runny nose and the presence of discharge in the nasal passages
- Assess congenital or trauma-induced deviation of the nasal septum
- Diagnose damage to the eardrum
- Study the adenoids, their size and condition
- Identify inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the nose, larynx and other areas, determine the source and etiology of inflammation
- Detect pathological neoplasms
- Examine the vocal cords for the presence of polyps, cysts, tumors or paresis
- Check the paranasal sinuses for tumors, polyps or inflammation
This method also helps to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment, check changes in the condition of the mucous membrane and the size of the formations.
General information about the procedure
Advantages of endoscopy in ENT practice
The advantages of endoscopic examination of ENT organs include:
- High detail. The endoscope provides the ENT specialist with an excellent overview of internal structures, including hard-to-reach areas. The ability to zoom the image and additional lighting allow you to accurately determine the nature of detected pathologies
- Lack of preparation. The procedure can be performed at any time during a visit to the doctor
- Instant results. The study takes place in real time, allowing patients to observe the process together with the doctor and immediately receive an opinion from him
- Comfort. Modern endoscopes are considered minimally invasive, making the procedure acceptable for most patients
- Safety. The procedure does not involve radiation exposure, so it is not harmful to health
- Efficiency and speed. The duration of endoscopy is comparable to a conventional examination of the nasopharynx, but provides much more information about the patient's condition
Many endoscopic procedures can be performed under local anesthesia, making them accessible to those patients for whom general anesthesia is contraindicated.
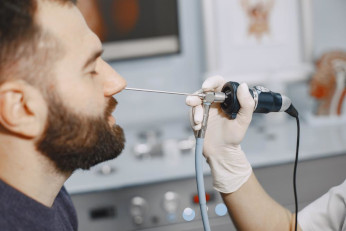
Types of endoscopic operations
In modern ENT practice, the following endoscopic operations are performed:
Endoscopic examination of the nose and nasopharynx is a procedure that allows the doctor to examine the inside of the nose and nasopharynx using an endoscope to diagnose diseases
Endoscopic polysinusotomy - sinus surgery performed through the nasal passages to restore normal drainage and ventilation of the sinuses
Endoscopic septoplasty – correction of a deviated nasal septum to improve nasal breathing
Endoscopic adenotomy - removal of enlarged adenoids (nasopharyngeal tonsil) through the oral cavity. Performed to improve breathing or reduce the incidence of infections
Endoscopic turbinate vasotomy is a procedure aimed at reducing the size of the turbinates to make breathing easier through the nose. Performed by cutting or coagulating (cauterizing) the vessels supplying the turbinates
Full recovery after endoscopic surgery takes from 5 to 20 days.
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services


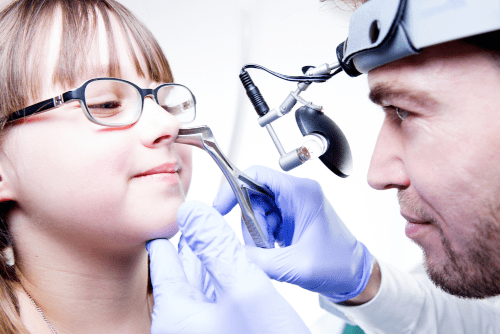
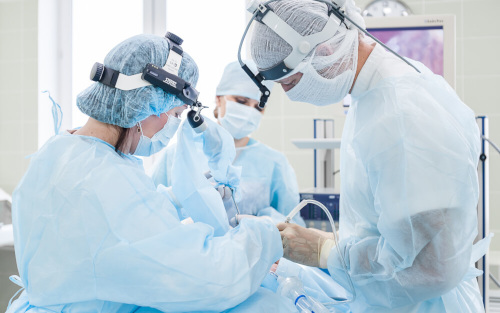




































The essence of the technique
Endoscopy of ENT organs allows you to study in detail the internal structures of the ENT organs using an endoscope. Control is carried out using a handle with a rotating mechanism. The area under study is displayed on the screen in high resolution.
Modern endoscopes can be equipped with tools such as biopsy forceps, knives for cutting tissue and special loops for removing formations. They allow surgery to be performed through small openings, minimizing trauma.
During the procedure, the doctor analyzes the condition of the ear, nose and throat in real time. He also examines the mucous membrane in detail, identifying features and changes. The study is necessary to assess the condition of the tonsils and auditory tract in children with adenoiditis.