Audiometry

specialists
equipment
treatment
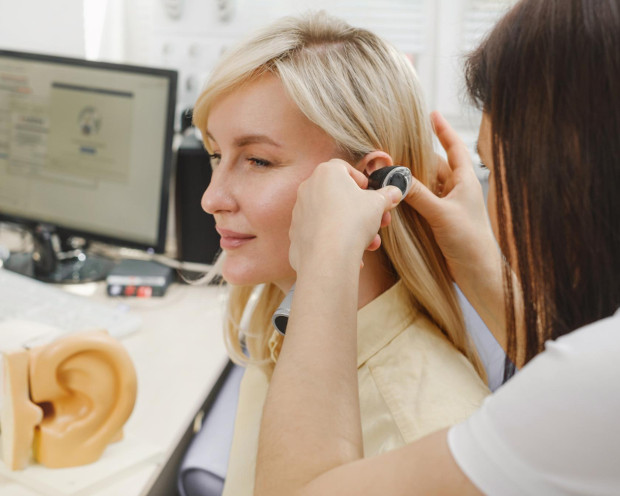

Why is audiometry necessary?
An audiometry test is recommended when the first signs of hearing changes appear: hearing loss, a feeling of "full ear," difficulty understanding speech, or constant noise. This test helps the doctor, rather than guessing based on complaints, rely on precise data: assessing the degree of hearing loss and determining at what stage additional diagnostics are needed or whether treatment is already necessary. Audiometry is often prescribed for follow-up after therapy (for example, after an ear infection or medication), for selecting and adjusting a hearing aid, and as a preventive screening for work-related or age-related risks. During the appointment, the doctor explains the results in simple terms and provides a treatment plan – and a timely examination allows for early detection of changes, when they are easier to correct. Additionally, audiometry helps document the initial hearing level so that objectively comparisons can be made after treatment or rehabilitation.
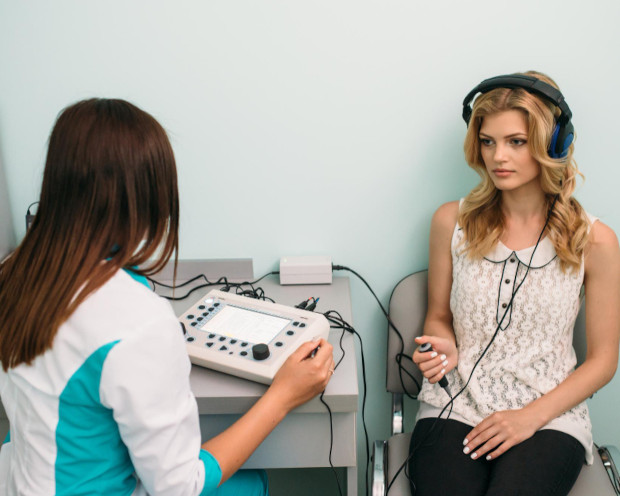

Types of audiometry
There are several types of audiometry:
- Live speech listening. The doctor moves away from the patient and speaks words at varying volumes. Hearing is assessed based on the patient's responses. The objectivity of the results is limited because it is impossible to precisely control the voice volume.
- Objective audiometry. Focuses on studying unconditioned reflexes that occur in response to sound. This method provides objective data on hearing status without the need for verbal responses from the patient.
- Speech audiometry. Helps determine how the patient perceives live or digitally recorded speech. This method is important for assessing the patient's ability to understand speech clearly in different conditions.

- Threshold and pure-tone audiometry. This determines how well a patient hears sounds of different frequencies. This allows for the determination of the minimum volume at which sound is still perceptible.
- Suprathreshold audiometry. This is used to assess hearing in patients with severe impairments. It helps establish the minimum volume at which sound becomes audible.
- Computer audiometry. This is a modern procedure that uses specialized software and equipment for detailed hearing assessment. This allows for automation and increased measurement accuracy.
- Pediatric audiometry. This is adapted for young patients, including infants and children under three years of age. A unique feature of this method is that the doctor evaluates hearing even in those who are unable to independently communicate their sensations.
Each of these methods has its own characteristics and is selected depending on the patient's age, their condition, and the doctor's goals.
How is speech audiometry performed?
Speech audiometry is a hearing test performed in a quiet room. The patient listens to words through headphones or speakers and repeats them into a microphone. Using an attenuator, the doctor adjusts the volume to find the quietest level the patient can still hear. The results are recorded, indicating the sound intensity and percentage of correct answers.
The procedure lasts 1.5 hours. The results describe three indicators: the hearing threshold (when the patient hears 50% of words), maximum intelligibility (when the patient understands 90% of words), and the discrimination level, which shows how well the patient distinguishes words at different loudness levels.
Features of tonal and threshold audiometry
An audiometer and headphones are used during the procedures. A bone vibrator and microphone are also required for pure-tone audiometry. The audiometer plays sounds of varying loudness and pitch (from 125 to 8000 Hz). The goal of the test is to find the loudness that causes discomfort.
The patient listens to the sounds through headphones in a soundproof room. If they hear them, they press a special button. If they don't, the doctor increases the volume until they hear them. This determines the lowest and highest loudness the patient can hear. The results are recorded on an audiogram.
How is suprathreshold ENT audiometry performed?
If a person is almost completely deaf, suprathreshold audiometry is performed. The patient is presented with a sound through headphones that is 20 dB louder than their hearing threshold. The volume is gradually increased, and the patient describes all their sensations. The doctor determines whether these correspond to reality.
Features of computer audiometry
Features of Computer Audiometry
The test does not require active patient interaction, making it suitable for people who cannot understand what is being asked of them. The procedure is also performed on paralyzed patients and small children.
Please note! To ensure patient calm and obtain accurate results, doctors sometimes use sedatives. The procedure is performed while the patient is asleep or under light sedation.
Before the test, electrodes are placed on the patient's head and connected to a computer. They also wear headphones, through which sounds of different tones and volumes are played. The computer analyzes how the brain responds to these sounds and records the results as a graph. This graph helps the doctor determine whether there are hearing problems and which part of the brain is damaged.
How is audiometry performed in children?
Child hearing testing is a challenging task. Children may not notice a problem or even mention it. Furthermore, maintaining their attention and focusing during testing can be challenging.
Doctors use special methods for very young children (even newborns). During the first examination, which is performed on the 3rd or 4th day of life, the doctor examines the ears from the outside. Tympanometry is then performed—a diagnostic method that involves using a probe to check the middle ear and eardrum. This allows for the detection of inflammation, fluid accumulation, perforation, and other abnormalities. The next important step is an otoacoustic emission test. This procedure is designed to elicit a response in the ear to sound. This allows the doctor to determine the problem and the appropriate correction method.
For children aged 3 to 5, audiometry becomes a game. The child hears a sound through headphones and is asked to respond, such as raising a hand. In this way, doctors test the hearing of each ear separately.
Schoolchildren undergo the same studies as adults. But even here, it's important to find an approach that keeps the child from getting tired and losing interest.
Why is audiometry performed in children's sleep?
When examining hearing in young children, doctors face certain challenges. Unlike adults, children cannot follow instructions or answer questions, making standard hearing testing methods unsuitable. In this case, a method known as sleep audiometry comes to the rescue. This procedure has been widely used since 1974 and has proven effective in assessing the hearing status of newborns and infants.
Why is sleep necessary? During the test, electrodes attached to the child's skin record the electrical impulses traveling from the ear to the brain. These signals are very weak, and to detect them, it is necessary to minimize all possible noise and interference. Sleep significantly reduces brain activity and reduces eye and muscle movement, making it easier to record auditory signals.
Audiometry for tinnitus and head noise can also be performed during sleep. For older children, starting from 7-10 years old, the test can be performed while the child is awake, provided they are completely calm and relaxed. However, this is not always feasible, especially if the child has certain medical conditions.
Audiometry for sensorineural hearing loss and impedance audiometry can also be performed while children are asleep to obtain the most accurate results. These methods help doctors thoroughly examine the child's hearing and determine the best methods for correction or treatment.
Parents who need audiometry for their children in Moscow should contact the K+31 Clinic. We have everything necessary for computerized audiometry. To find out the cost of the test, call us at the number listed on the website.
Indications for audiometry
Infants are screened for congenital hearing and nervous system disorders. Furthermore, if a patient has a history of ear disease and is considering cochlear implantation, audiometry helps select and adjust the appropriate hearing aid. After ear surgery, this test helps determine whether hearing has improved. People working in noisy environments should have audiometry regularly, at least once a year.

It is important for those who are faced with:
- Inflammatory diseases of the ear (otitis, labyrinthitis, mastoiditis)
- Neuroinfections, such as meningitis or encephalitis
- Head injuries
- Tumors of the brain or ear
- Inflammation of the auditory nerve
- Hearing loss of unknown origin
The procedure is not recommended for people with mental disorders or inappropriate behavior. Pure-tone and threshold audiometry are not performed on newborns or patients paralyzed after a stroke, as they are unable to follow doctor's instructions. In these cases, computerized audiometry is used.
General information about the procedure
Audiometry prices in Moscow
The price of audiometry depends on the examination format and diagnostic objectives. The cost is influenced by the specific test type (tone, speech, or computer), whether the examination is being performed on an adult or a child, and whether a doctor's consultation and extended interpretation of the results are required. The final cost is usually determined after clarifying the patient's complaints and selecting the optimal protocol.

Answers to popular questions
Who does the hearing test?
What is the difference between an audiogram and audiometry?
What are the alternatives to audiometry?
An alternative to audiometry is impedance measurement. This is an automated method that helps evaluate the condition of the middle ear, including the eardrum and auditory tube. The procedure involves inserting a probe into the ear, which creates pressure and produces sounds. A special microphone analyzes the response of the eardrum to these influences.
Nuance! Impedance testing does not assess sensorineural hearing impairment or the condition of the inner ear.
This method is good for detailing the condition of the outer and middle ear, especially if questions arise after audiometry or a more accurate diagnosis is required.
K+31 photo gallery

Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services
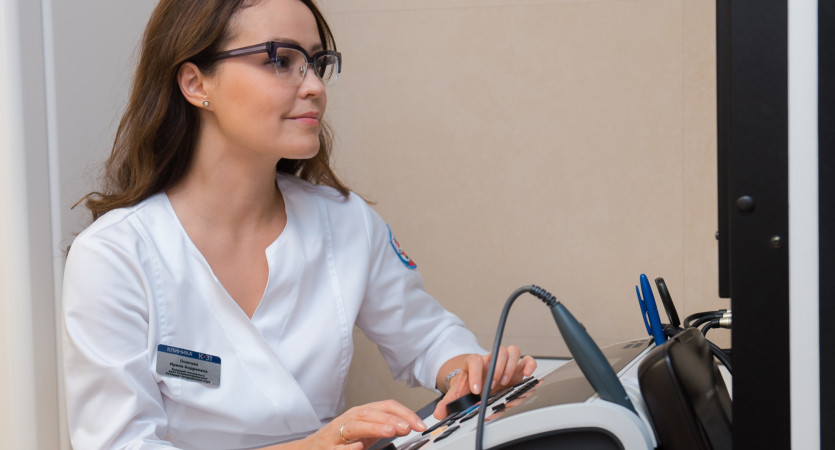









































What is audiometry?
Audiometry is a medical method used to diagnose hearing and helps accurately assess how a person perceives sounds of different frequencies and loudness. During the procedure, hearing thresholds are recorded—what soft and what high/low sounds the patient can distinguish—and the results are recorded as an audiogram. Unlike everyday "checks" (where you think you hear normally), this is a standardized test that reveals real changes and their extent. Audiometry is used in clinical practice to confirm hearing loss, determine treatment strategies, monitor progress, and determine whether additional diagnostics or rehabilitation is needed.