Removing wax plug

specialists
equipment
treatment

Indications for removal of wax plug
- Deterioration of hearing or sudden loss
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
- Pain in the ear canal
- Frequent ear infections
- Noise or ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Headache, dizziness and balance problems
- Reflex cough, vomiting
- Unpleasant odor from the ear
- Discomfort when wearing hearing aids or headphones
Signs of an ear plug
At the beginning of the formation of an ear plug, a person usually does not feel any discomfort. The first symptoms occur after water gets into the ear canals, for example, while swimming or showering. Water turns the sulfur into a soft, playdough-like mass that attaches to the eardrum and impairs hearing.
Other signs of wax plug formation include:
- Feeling of ear fullness
- Deterioration in the ability to perceive sounds
- Echo of your own voice in your head
- Painful sensations in the ears
- Noise or humming occurs
If the plug puts pressure on the eardrum, additional symptoms may appear. Among them are reflexive cough, headaches, nausea, dizziness. If you notice the first symptoms, it is recommended to immediately consult an otolaryngologist to avoid inflammation and other complications.
Diagnostic methods
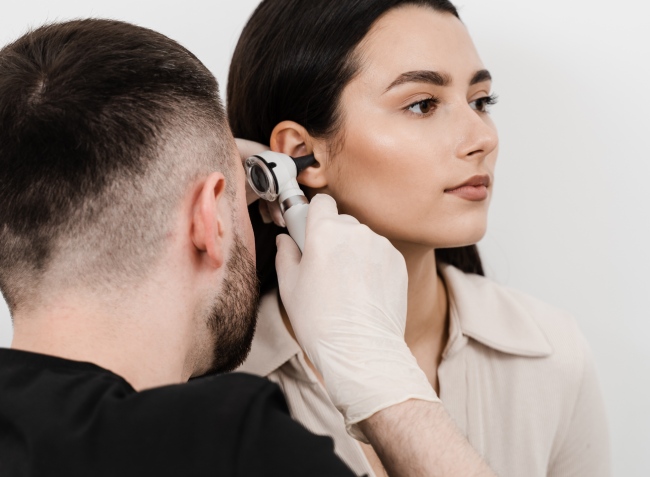

No complex laboratory tests are required to identify ear plugs. The doctor analyzes the patient's complaints and conducts an examination. Large plugs are visible without special equipment, but for small ones a painless and comfortable technique is used - otoscopy. Using a frontal reflector and a special funnel, the doctor examines the ear canal. Sometimes the procedure causes a reflex cough due to nerve irritation.
The doctor must also distinguish between wax plugs and other diseases:
- Otomycosis - fungal infections of the ear, which are accompanied by characteristic discharge
- Cholesteatomas, or epidermal cysts formed from dead skin cells and containing no earwax
- Tumors in the ear canal
- Foreign bodies in the ears, which is common in children
Before and after the wax removal procedure, hearing function is assessed. It is carried out by testing the patient's ability to detect a whisper at a distance of 6 meters or using a tuning fork.
If hearing is not restored after removing the plug, additional examinations are prescribed, including pure tone threshold audiometry. In this test, the patient listens to sounds of different frequencies through headphones in a soundproof room, noting the audibility of each of them.
Removing wax plugs from ears
How to properly care for your ears
After the procedure, the doctor gives recommendations on caring for the ears:
- Use cotton swabs correctly. Limit their use to the outer part of the ear. Avoid deep penetration into the ear canal. Choose models with limiters
- Explain to your child that small objects should not be inserted into the ears
- Seek medical help promptly. If infectious diseases or unpleasant symptoms appear in the ears, immediately make an appointment with a doctor
- Avoid removing wax plugs yourself. Only a qualified doctor will perform the procedure safely
- Get preventive examinations to prevent chronic ear diseases
When bathing or swimming, wear protective equipment (such as waterproof earplugs) to prevent water from entering the ear canal.
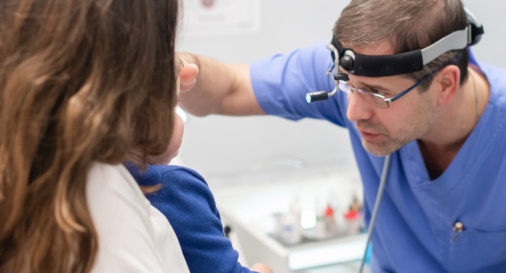
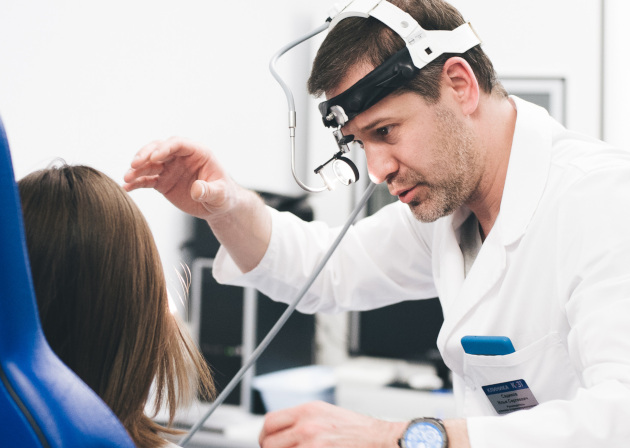
How is an appointment with an otolaryngologist at K+31?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services

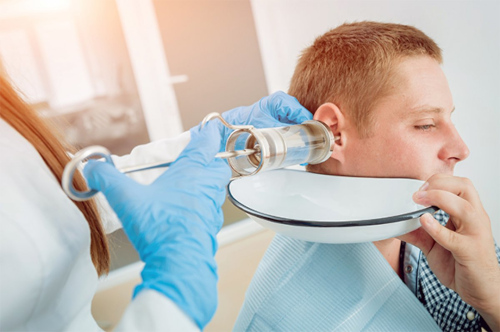
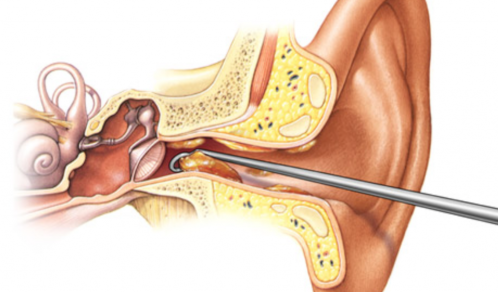
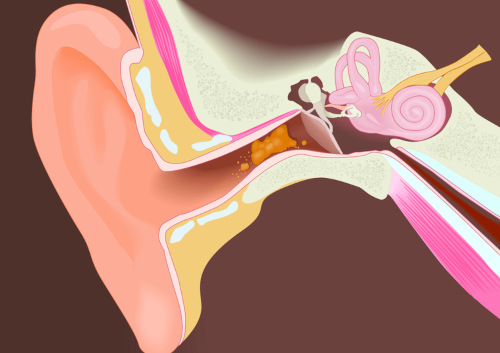


































Causes of ear plugs
Earwax is an accumulation of earwax and dead cells in the ear canal, which interferes with the normal perception of sounds. According to statistics, about 5% of the population faces this problem. The actual number may be higher because not all people seek medical help.
The formation of ear plugs is promoted by internal and external factors. Internal factors include:
Among the external factors, doctors highlight the regular use of cotton swabs to clean the ears, the use of headphones, hearing devices and protective earplugs. Also, the risk of traffic jams increases when working in environments where there is a lot of dust.
Due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the ear canals, children and the elderly are most susceptible to the formation of wax plugs. Also, excessive accumulation of secretion from the sebaceous glands is observed in chronic diseases, otitis media, eczema, and incorrect apposition of the upper and lower jaws.