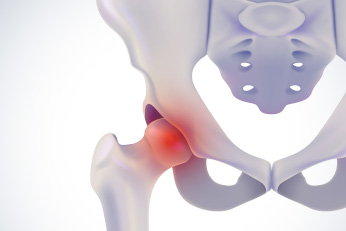
Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head
ASPH is a severe condition in which bone tissue dies due to insufficient blood supply. The condition can develop at any age, but is most often diagnosed in men aged 30-50. This tendency is caused by unhealthy habits and intense physical activity.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Causes of aseptic necrosis
The disease occurs for various reasons related to impaired microcirculation, mechanical stress, injuries, and metabolic disorders.
Causes in childhood
In children, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head is called "Perthes disease." This pathology occurs due to the following causes:
- Disruptions in the embryonic development of the femoral vessels
- Genetic predisposition
- Pelvic and hip injuries
- Hormonal imbalances during the period of active growth
- Autoimmune processes
In a weakened immune system, infectious diseases can trigger aseptic necrosis.
Causes in adulthood
In adult patients, the disease develops under the influence of the following factors:
- Hip joint and femur injuries — fractures, dislocations, severe bruises — disrupt blood supply, which triggers the necrotic process.
- Alcohol abuse — causes the formation of fatty microthrombi in blood vessels, disrupts tissue nutrition.
- Blood and vascular diseases — vasculitis, hypercoagulability, thrombophilia lead to deterioration of microcirculation.
- Metabolic disorders — diabetes mellitus, obesity, hyperlipidemia reduce vascular tone, worsen bone tissue condition.
- Infections — septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, hepatitis B and C viruses, tuberculosis of bones and joints cause vascular stenosis and circulatory impairment.
Rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis, systemic erythematosus Lupus and antiphospholipid syndrome also contribute to the development of vascular changes.
Causes in old age
Causes in elderly patients are due to age-related changes. These include:
- Decreased vascular quality – atherosclerotic plaques narrow the lumen of blood vessels and impede blood flow
- Decreased bone density – bones become more vulnerable to fractures and destruction
- Concomitant chronic diseases – hypertension, heart failure
- Decreased tissue regenerative capacity – slows the recovery of damaged bone areas
- Increased risk of injury due to decreased coordination and balance – frequent falls and bruises
Long-term use of anticoagulants, chemotherapy drugs, and diuretics can negatively impact metabolism and vascular health.
Symptoms of aseptic necrosis
The clinical presentation depends on the stage of the disease. Main symptoms include:
- Pain in the groin, buttock, and knee, which intensifies with walking.
- Limited hip mobility.
- Limping, limb shortening.
- Muscular atrophy of the hip.
- Pinching in the joint when turning the leg.
Pain may appear suddenly or develop gradually. In the early stages, it subsides with rest. As the disease progresses, the pain becomes constant.
Stages of aseptic necrosis
Knowledge of the disease's stages allows the doctor to assess the extent of joint damage, predict its further development, and choose treatment options.
-
Stage 1
The initial stage is characterized by impaired blood supply without structural changes to the bone tissue. X-rays do not reveal any abnormalities, but MRI may reveal bone marrow edema. Pain is episodic.
-
Stage 2
Necrotic foci form, visible on X-ray as lumps or cysts. The pain intensifies and occurs with even the slightest exertion. Mobility is limited, and the patient cannot bear weight on the affected leg.
-
Stage 3
The femoral head begins to deform, and cracks appear. The pain becomes constant and intensifies with walking. Mobility is severely impaired.
-
Stage 4
Complete destruction of the articular surface, severe pain, significant limitation of motion, and secondary arthrosis. The limb is shortened, and muscle atrophy develops. Walking without support is virtually impossible.
Diagnosis of aseptic necrosis
To establish an accurate diagnosis, a comprehensive examination is required. This includes:
- X-ray — used to assess bone deformities in stages 2-4
- MRI — the most sensitive method in the early stages, allowing for the detection of bone marrow edema and necrosis.
- CT — allows for a detailed assessment of bone structures.
- Bone scintigraphy — used to study bone metabolism.
Laboratory tests are performed to rule out infectious arthritis and assess the overall condition.
It is important to distinguish ANFH from other pathological conditions:
- Osteoarthritis of the hip. This is accompanied by pain and limited mobility. There is no primary circulatory disorder; symptoms develop gradually.
- Coxitis. This occurs with rheumatic diseases, injuries, and infections. It is characterized by severe swelling, increased temperature in the joint area, and general intoxication.
- Femoral neck fracture. This is accompanied by severe pain, inability to bear weight on the leg, and deformity, which is confirmed by X-ray.
- Tendinitis and bursitis. These cause pain that radiates to the hip joint. There are no changes in bone tissue or circulatory disorders.
- Tumors of bone and soft tissue. They cause pain and limited movement.
Radiating pain in the hip area may be due to damage to the nerve roots or spinal cord, rather than the joint itself. A neurological examination and imaging techniques can help differentiate these pathologies.
Treatment of Aseptic Necrosis
Treatment is aimed at maximizing joint function and improving patients' quality of life.
Conservative Treatment
Stops destructive processes. Used for minor structural changes in the femoral head. Conservative treatment involves drug therapy and physical therapy. Let's take a closer look.
Drug Therapy
The course includes the following medications:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Reduce inflammation and pain, improve joint mobility, and alleviate discomfort. For severe pain, stronger analgesics are used under a physician's supervision.
- Vascular medications. Enhance blood microcirculation, improving tissue oxygen and nutrient supply.
- Anticoagulants and antithrombotic drugs. Reduce the risk of blood clots, which can worsen impaired bone blood supply.
- Vitamin complexes. Calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, and phosphorus supplements are indicated for strengthening bone tissue. B vitamins improve nerve conduction and metabolic processes.
In some cases, bisphosphonates and drugs that stimulate osteogenesis (the process of bone formation) are used. Their use requires careful medical supervision due to possible contraindications and the risk of side effects.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures are used both as part of conservative therapy and after surgery. Their main goals are:
- Improved blood circulation
- Stimulated bone and cartilage regeneration
- Relieved inflammation
- Pain relief
Regular physiotherapy slows the pathological process and increases the effectiveness of drug treatment. Orthopedists most often prescribe the following procedures:
- Magnetotherapy. A low-frequency magnetic field has a vasodilating and anti-inflammatory effect, improves microcirculation and metabolic processes in the affected area. The procedure is painless, well-tolerated by patients, and is used at all stages of the disease.
- Laser therapy. Low-intensity laser radiation stimulates cellular metabolism, improves tissue nutrition, and accelerates the restoration of damaged bone areas. In addition, the laser has a pronounced analgesic effect.
- Ultrasound therapy. Ultrasound exposure increases the permeability of cell membranes and activates local blood flow.
- Medication electrophoresis. Allows the delivery of analgesics, vascular, and anti-inflammatory agents directly to the lesion using electric current.
- Paraffin-ozokerite applications. Local thermal exposure relaxes muscles, improves blood circulation, and reduces pain. It is most often used in the subacute stages and during the rehabilitation period.
A physiotherapy course includes 10-15 sessions, performed daily or every other day. Each session lasts from 10 to 30 minutes. The total course of treatment lasts 2-3 weeks. If necessary, the course is repeated with a break of 1-2 months.
Orthopedic Regimen
Aimed at reducing mechanical stress on the hip joint, slowing femoral head deterioration, and stimulating recovery processes. Doctors recommend:
- Avoid prolonged walking, standing, climbing stairs, and carrying heavy objects. This prevents microtrauma.
- Use additional support. Canes, crutches, and walkers redistribute body weight, reducing pressure on the joint.
- Avoid jumping, running, and brisk walking. These accelerate wear on the articular surface.
- Use orthoses. Orthopedic devices maintain the joint in the correct position, reduce range of motion, and relieve pain.
During the day, it is important to alternate periods of moderate physical activity with adequate rest. Prolonged immobility contributes to blood stagnation and poor bone nutrition. The optimal regimen is 30-40 minutes of activity, followed by 15-20 minutes of rest in a supine position with legs elevated.
Important! Sleeping on your back or on the unaffected side with a pillow between your knees to stabilize the hip joint is recommended. This reduces the risk of microtrauma and morning stiffness. Rise from bed slowly, using additional support.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgery is indicated. The main surgical treatment methods include:
- Decompression. In the affected bone, the doctor creates channels to reduce intraosseous pressure and improve blood flow. This activates natural bone regeneration and slows the necrotic process. The technique is used in the early stages of the disease. Osteotomy. This involves changing the position of the femur to redistribute the load to less damaged areas. It allows for temporary preservation of the natural joint in, postpone endoprosthetics.
- Transplantation. Sections of healthy bone tissue with a vascular network are transplanted into the necrotic area to restore the structure and nutrition of the affected area. This technique is used in more severe cases, but before complete deformation of the head.
- Endoprosthetics. The destroyed joint is replaced with an artificial implant. It is used in later stages, when joint preservation is impossible.
When choosing a surgical method, the patient's age, the stage of aseptic necrosis, and the general condition of the body are taken into account.
Why you should contact specialists
The orthopedist will prescribe the necessary examinations, select the optimal treatment plan based on your lifestyle, profession, and associated conditions, and monitor your recovery. At the slightest sign of progression, the doctor will adjust the therapy. Self-medication can worsen the condition and cause irreversible changes in the joint.

Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to cure aseptic necrosis without surgery?
Yes, in the early stages, the disease can be treated conservatively. The main thing is to follow the regimen, take your medications, and follow your doctor's recommendations.
How long can you live with aseptic necrosis?
Life expectancy depends on the extent of the disease and overall health. If the disease does not progress, the patient can live with it for a long time without significant limitations. If symptoms worsen, surgical intervention is required.
Is it possible to play sports with ANFH?
Yes, but not all sports. Running, soccer, jumping, and tennis are prohibited. Boxing, kickboxing, taekwondo, karate, freestyle wrestling, and judo are also prohibited. Physical therapy, swimming, and cycling are recommended.
What are the possible consequences of refusing treatment?
Progression to arthrosis, complete loss of mobility, the need for prosthetics, and disability.
Is it possible to drive a car with ANGBK?
Yes, it's possible in the early stages. If the pain is severe or after surgery, driving can be resumed only after full rehabilitation and clearance from a doctor.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services































































General information
Avascular necrosis of the femoral head is a relatively rare condition. According to statistics, the disease occurs in approximately 10-20 people per 100,000 population per year and accounts for approximately 10% of all musculoskeletal disorders.
If you notice pain and limited mobility, contact the K+31 clinic in Moscow. Our experienced doctors will, after a thorough diagnosis, prescribe effective treatment for avascular necrosis of the femoral head. You can view service costs and schedule an appointment online or by phone.