Prostate adenoma
Do you frequently need to urinate, and is urinating accompanied by discomfort? It's possible you have an adenoma of the prostate gland. You can undergo comprehensive diagnosis and treatment for this condition at the multidisciplinary clinic "K+31" in Moscow.
Adenomas are benign tumors that originate from glandular epithelium.

specialists

equipment

treatment

Appointment to the doctor
Prostate adenoma in men: symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment
Early symptoms of prostate adenoma include minor urinary disturbances.
Clinical manifestations
Daytime urgency increases significantly during the first stage, and at night the patient must wake up at least 1-2 times to use the restroom.
In the morning, the patient must tense the abdominal muscles to begin emptying the bladder, and the urine stream becomes weak. Urgent urges, accompanied by the passage of a small volume of urine, are occasionally observed.
During the subcompensation stage, daytime and nighttime urgency increases, the volume of urine excreted decreases, and the amount of residual urine exceeds 50 ml. The urine stream becomes unstable (sometimes increasing, sometimes decreasing), and during this process, the patient must constantly tense the abdominal muscles.
Dripping (dripping) occurs between visits to the restroom. Congestion can lead to the development of infectious and inflammatory complications, such as cystitis and/or urethritis.
The leading symptom of adenoma in the decompensated stage is pathological urinary retention. A man constantly feels the need to urinate, but even with maximum abdominal muscle tension, the process is extremely difficult.
Urine is excreted almost constantly, dribbling. Its stagnation leads to dilation and inflammation of the renal pelvis, as well as compression of the renal parenchyma.
Again, symptoms of renal failure appear: dysuria, peripheral and central edema, thirst, dry skin, loss of appetite, nausea, hypertension, rapid heartbeat, and flatulence.
Diagnostics
If signs of prostate pathology appear, you should consult a urologist. To establish a diagnosis, the doctor first collects a medical history.
A digital rectal examination is performed to obtain a preliminary assessment of the prostate's size. An ultrasound scan can help determine the extent of pathological tissue growth and the degree of urethral compression. It is most often performed transrectally, i.e., with the insertion of a probe into the anus. Transabdominal ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the kidney structures.
To verify the diagnosis and objectively assess the condition of the kidneys and bladder, a urethrocystoscopy and urodynamics (uroflowmetry) are prescribed.
The patient is always referred for laboratory blood testing. The level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is determined, which helps distinguish adenoma from a malignant neoplasm.
Please note: PSA is a key cancer marker. Its blood concentration increases significantly if prostate cancer develops.
If test results are inconclusive, a prostate biopsy followed by cytological and histological examination of the biopsy specimen is recommended. This method allows us to rule out cancer.
Treatment methods
With timely initiation of therapy, it is possible to halt the progression of the pathological process. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is unavoidable, and treatment for renal failure will also be required.
The choice of patient management tactics depends on the etiology, stage of the disease, and clinical symptoms. Conservative treatment includes the use of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (Dutasterone, Avodart), herbal remedies (in the form of rectal suppositories), and α-blockers (Silodosin, Doxazosin, etc.).
If infectious complications are detected, a course of antibiotic therapy is administered. Antispasmodic medications are also indicated.
Surgical treatment of prostate adenoma involves tumor removal, as well as partial or complete resection of the gland. Indications for surgery include stages 2 and 3 tumor progression and the risk of cancer development.
Types of surgery:
- Laser vaporization or enucleation
- Transurethral resection
- Adenomectomy
Vaporization is the "evaporation" of the affected structures. This minimally invasive technique is indicated for young patients, since the procedure does not affect fertility.
Laser enucleation can be used for large tumors. This method involves enucleating tumor structures from the gland.
During transurethral resection, an endoscope is inserted into the urethra. During the procedure, the adenoma is removed along with a fragment of the gland. Adenomectomy involves removing only the tumor itself.
Rehabilitation period
Minimally invasive procedures allow the patient to be discharged home within a few hours after surgery. During the first few weeks, patients should drink at least 3 liters of fluid per day, but not after 6 p.m. Constipation-causing foods should be excluded from the diet. If intestinal motility is reduced, laxatives should be taken.
For one month after surgery, it is recommended to avoid hot baths (showers are recommended) and swimming in bodies of water (to avoid infection). Physical activity should also be avoided for 2-4 weeks.
Sexual abstinence is recommended for the next six weeks. Postoperative treatment at a spa is recommended.
Preventive measures

It is important for men of all ages to understand what an adenoma is, its potential danger to the body, and how to prevent tumor development.
Important: With advancing age, the risk of adenoma becoming malignant increases. Therefore, men over 50 are advised to strictly follow their urologist's instructions and undergo regular testing (in particular, PSA testing).
It is important for all men to promptly treat reproductive system pathologies, without waiting for complications to develop.
Key prevention methods:
- Take special vitamin and mineral supplements (prescribed by a urologist-andrologist)
- Give up bad habits
- Regular sexual activity
- Medical examinations with a urologist (after age 45 - at least once a year)
- Weight control
- Proper nutrition
- Blood pressure monitoring
- Active lifestyle
- Minimize the impact of stress factors
- Maintain a work and rest schedule

Measured physical activity helps prevent pelvic congestion, which can negatively impact the genitourinary system.
To detect a dangerous condition early, visit a urologist at the K+31 Clinic. You can schedule an appointment by phone or online. Comprehensive diagnostics are performed using high-precision equipment and modern laboratory tests.
Our clinic has a balanced pricing policy, a loyalty program for regular clients, and regular promotions. We guarantee complete confidentiality to our patients. Information about their sensitive condition will never be shared with outsiders.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Reviews

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.






















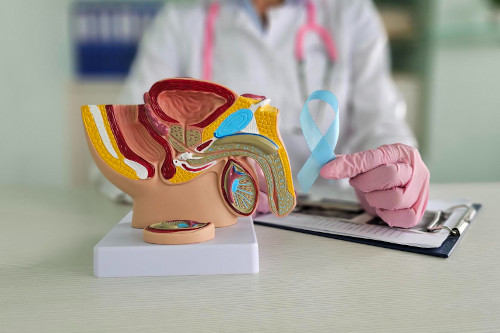























What is prostate adenoma?
The normal size of the exocrine gland is approximately the size of a walnut. It produces a special secretion that increases sperm fluidity and ejaculate volume.
BPH is a benign tumor that develops due to hyperplastic changes in the structures of the male reproductive system.
Statistics: Among men over 40, the incidence rate is over 25%, and among patients 50 years and older, the prevalence reaches 50%.
BPH is not a cancerous tumor, but there is a risk of malignancy (i.e., malignant transformation).
This condition is characterized by diffuse changes in the prostate gland. The growth of tissue structures leads to compression of the urethra and dysuria.
Due to urinary stasis, the risk of developing urinary tract diseases significantly increases.
These include:
Please note: It is important to understand the difference between prostate adenoma and prostatitis. Adenoma is an overgrowth of glandular tissue, while prostatitis is an inflammation that can be caused by various factors (including genital tract infections).