Chickenpox Treatment in Children
The doctors at the K+31 Medical Center provide qualified care to young patients with the acute viral infection known as chickenpox in children, regardless of the form and severity of symptoms. We use modern, evidence-based approaches and adhere to current clinical guidelines from the Russian Ministry of Health.
Our treatment programs for young patients are aimed not only at relieving unpleasant symptoms but also at preventing complications, accelerating recovery, and ensuring competent infection control under the supervision of a pediatrician and infectious disease specialist.

specialists

equipment

treatment
The cause of chickenpox in children

The etiologic agent is Varicella Zoster. This is one of the most contagious viruses: infection is likely through close contact in the overwhelming majority of cases. After penetrating the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, the pathogen spreads lymphohematogenously and attacks epidermal cells, leading to:
- Vesicle formation
- Fever
- Itching
The greatest number of cases is recorded in organized settings: kindergartens, schools, and sports clubs. The peak age is approximately 2–10 years. In infants (in the presence of maternal antibodies) and adolescents over 14, the course of the disease may differ: in the former, it is milder, while in the latter, it often involves severe intoxication and a profuse rash.
How does infection occur and the incubation period?
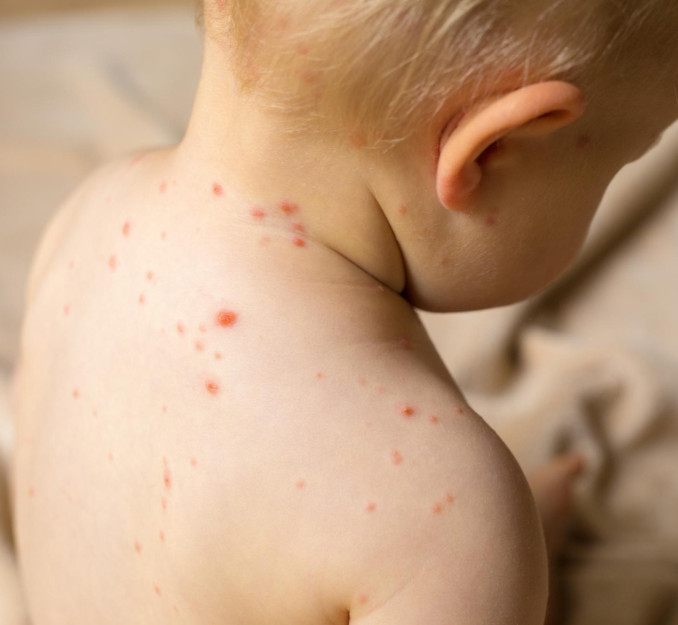
Our specialists remind you that this infection is extremely contagious. Air currents in a room easily carry aerosols over significant distances. In organized groups, a single episode is enough to infect almost all non-immune children.
How can you become infected with chickenpox?
The primary route is airborne. Infection is possible through talking, coughing, and sneezing. The pathogen can travel with air currents, which explains family and group outbreaks. After penetrating the mucous membranes, the virus enters the bloodstream and then the skin, where vesicles form.
A child becomes contagious 1-2 days before the rash appears and remains infectious until the last scab falls off. Therefore, isolation and notification of a pediatrician are recommended.
Incubation Period and Contagiousness of Chickenpox
The period from exposure to the first symptoms is 10–21 days (usually about two weeks). The highest contagiousness occurs during the first 5 days after the rash appears. The risk of transmission decreases thereafter.
After infection, long-lasting protection develops. Recurrences are rare, but Varicella Zoster can persist in nerve ganglia and manifest as shingles years later.
Chickenpox Treatment in Children
Methods and stages of treatment
Most children are treated at home under the supervision of a pediatrician. Hospitalization is indicated for severe cases, high fever, complications, or a weakened immune system. Key components:
- Antipyretic therapy: paracetamol/ibuprofen at temperatures > 38°C; Aspirin is contraindicated in children (risk of Reye's syndrome).
- Skin care - gentle antiseptic treatment of affected areas (as prescribed by a doctor) to prevent secondary bacterial growth.
- Itching control - antihistamines, cool air baths, light cotton clothing.
- Regimen and hydration - adequate fluid intake, a gentle diet, normal sleep.
- Monitoring for complications - if signs of suppuration, difficulty breathing, or seizures appear, seek immediate medical attention.
Drug Therapy
Specific antiviral agents are not necessary for most children. In severe cases or in adolescents, acyclovir may be prescribed (most effective within the first 24-48 hours of the onset of the rash). Additionally, the following are used:
- Antipyretics in age-appropriate doses
- Antihistamines to reduce itching
- Topical antiseptics for skin treatment
- If indicated, supportive medications at the doctor's discretion
We adhere to the principles of evidence-based medicine: we exclude unnecessary prescriptions and focus on competent care and the prevention of complications.
Caring for Children with Chickenpox
Recommendations for Parents:
- Ensure a gentle regimen and isolation
- Change underwear and bed linen daily
- At normal temperatures, a short, non-friction shower is permitted; afterward, pat the skin dry with a soft towel.
- Avoid harsh detergents that can dry out the skin.
- Trim nails short to reduce the risk of scratching and infection.
K+31 specialists specifically emphasize: water treatments are permissible if the child feels well and there is no active skin inflammation.
Why is it better to treat chickenpox on K+31?
The K+31 team supports your child at every stage—from the initial consultation and diagnosis to full recovery and subsequent prevention.
- Experienced pediatricians and infectious disease specialists with up-to-date protocols
- Complete diagnostics, and, if necessary, 24-hour inpatient monitoring
- Individualized treatment plans and detailed care recommendations
- Prevention and management of complications
- Safe vaccinations in a convenient manner
Our goal is to ensure that our little patients recover from the infection easily and without complications, and that parents receive a clear, understandable action plan.

Questions and Answers
How long does an episode last?
Is showering allowed?
Does recurrence occur?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services









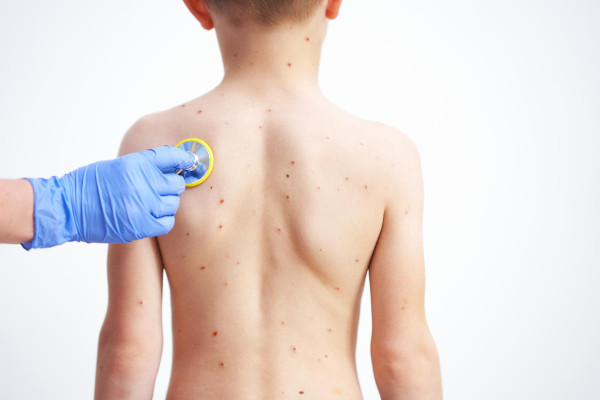

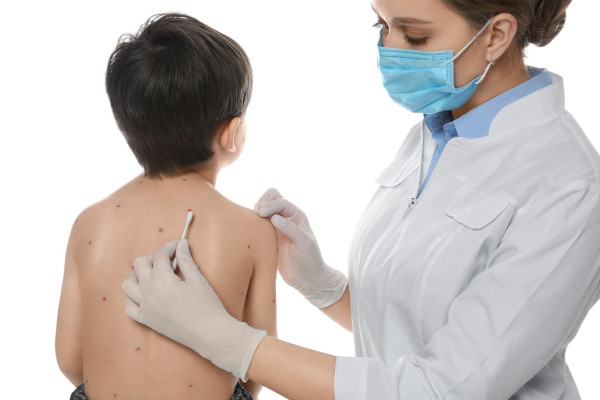


























































What is chickenpox in children?
Chickenpox is an acute disease caused by the Varicella Zoster virus, a member of the herpesvirus family. The pathogen is transmitted primarily by airborne droplets. The clinical picture is characterized by a vesicular skin rash, intermittent fever, itching, and signs of intoxication. The disease most often occurs in children, but episodes have also been reported in adolescents and adults, especially in those who lack immunity following vaccination or previous infection.
Most children have a benign course of the disease. However, children with a weakened immune response, chronic illnesses, or signs of a severe process require closer monitoring. At K+31, we thoroughly diagnose chickenpox in children, assess their overall condition, and develop an individualized treatment plan.