Treatment of inguinal hernia in children
Inguinal hernia in children is a condition in which a portion of internal tissue protrudes through an abnormally widened inguinal canal or a vulnerable spot in the anterior abdominal wall. The hernia does not resolve, but only increases in size, and therefore requires competent and timely treatment.

specialists
equipment
treatment
Causes of inguinal hernia in children
Pathological protrusions form for the following reasons:
- A congenital anomaly in which part of the peritoneum, descending along with the genitals into the inguinal canal and scrotum in boys (or into the labia majora in girls), does not close after birth as it should.
- Prematurity: In children born prematurely, the abdominal wall tissues and muscle structures are not yet fully formed, making them more vulnerable to hernia formation.
- Hereditary predisposition: The presence of an inguinal hernia in one or both parents increases the risk. There is a risk of hernia development in a child as well.
- Factors that increase intra-abdominal pressure include: loud and frequent crying, chronic coughing, constipation, straining, and increased physical activity. These factors can trigger or worsen the development of a hernia in both infants and adolescents.
Anatomy and pathogenesis
Normally, during the prenatal period, the fetus develops a vaginal process of the peritoneum—a thin sac through which the testicle descends into the scrotum in boys, and through which the ligaments move toward the labia majora in girls. After birth, this process should completely close. Otherwise, a connection with the abdominal cavity remains in the inguinal canal. Part of the internal organs may protrude through this canal, causing a hernial protrusion.
Over time, the hernia increases in size: its walls stretch, increasing pressure on the tissue. This increases the risk of strangulation, which disrupts the blood supply, and the organ may suffer from ischemia or necrosis. A strangulated hernia requires immediate medical attention.
Risk factors
Main risk factors:
- Premature birth
- Gender - boys are more likely to develop inguinal hernias.
- A history of inguinal hernia in parents or siblings.
- Connective tissue pathologies in the mother.
Risk factors allow doctors to assess the risk of inguinal hernia in a child and determine the need for early monitoring or preventive screening.
Classification and stages of the disease

The condition is classified according to several important characteristics, which helps the physician develop the correct treatment plan and assess the risk of complications:
Hernia types by anatomical features:
- Indirect hernias: pass through the inguinal canal
- Direct hernias: exit through a vulnerable area in the posterior wall of the inguinal canal
- Sliding hernias: part of the hernial sac is formed by the wall of an organ (for example, the bladder or intestine), which complicates diagnosis and surgery.
- Combined hernias: several unrelated hernial protrusions can exit through different areas of the inguinal region.
Hernias can be congenital or acquired by origin. A congenital inguinal hernia occurs due to the failure of embryonic structures to close. Acquired hernias form after birth. Hernias can also be reducible, non-reducible, or strangulated.

Stages of inguinal hernia in children:
- Initial (latent) stage. The bulge appears rarely and only with straining. There is usually no pain, but discomfort may occur with exertion.
- Moderate stage. The hernia is more clearly visible and may be noticeable when the child stands or moves. It is easily repositioned into the abdominal cavity and does not cause significant pain. This is the stage at which the disease is most often diagnosed.
- Progressive stage. The bulge increases in size, causing intermittent pain and discomfort with movement.
- Complicated stage (irreducible or strangulated hernia). The hernial bulge becomes dense, painful, and cannot be repositioned. The child may experience digestive symptoms, anxiety, vomiting, and fever. This is an emergency requiring immediate medical attention.
Symptoms of inguinal hernia in children
In the early stages, an inguinal hernia develops asymptomatically, making timely diagnosis difficult. Therefore, if any warning signs appear, it's important to take your child to a pediatrician and follow all recommendations.
Signs and symptoms
The main signs that can help identify this pathology are:
- A bulge or swelling in the groin area
- Pain, heaviness, or pressure in the groin area
- The bulge becomes increasingly firm and red—a possible sign of strangulation
- Voming, loss of appetite, bloating, or fever are signs of a complicated hernia that require immediate medical attention.
If any of these signs appear, it is important to consult a pediatrician or pediatric surgeon as soon as possible.
Strangulated hernia and its symptoms
Strangulation occurs when some of the internal organs remain in the hernial sac and cannot return to their original position. Without timely treatment, it can lead to bleeding and tissue necrosis.
The main symptoms of a strangulated hernia are:
- Sharp pain occurs in the area of the protrusion, and the skin in the affected area becomes swollen, red, or even bluish.
- A drooping abdomen, no stool or gas, and a deterioration in general condition.
- The child becomes irritable, refuses to eat, and may complain of nausea or vomiting.
Strangulation of a hernia is an emergency requiring immediate medical attention. If the above symptoms appear, consult a surgeon immediately.
Diagnosis of inguinal hernia
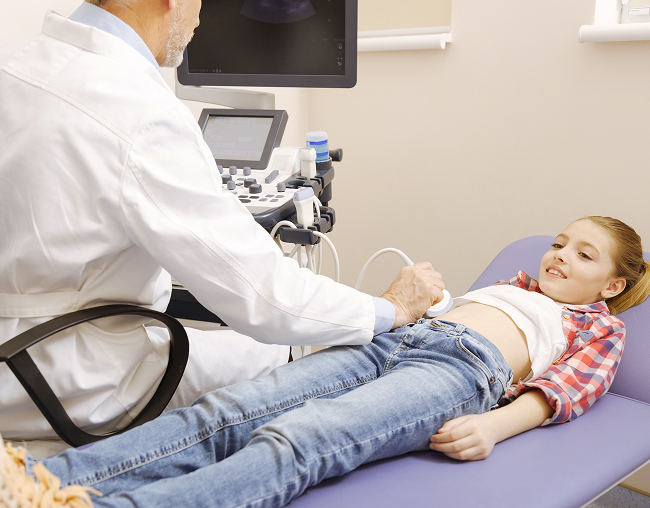
Diagnostics plays an important role in assessing the pathological process and prescribing treatment. Modern methods allow for the precise determination of the nature of the pathological protrusion and promptly perform all necessary procedures.
Diagnostic Methods
The following methods are used to establish a definitive diagnosis:
- Visual examination: the surgeon determines the presence of a protrusion both at rest and during straining.
- Palpation of the inguinal canal. The doctor attempts to reduce the hernial contents to assess the extent of the pathology.
- In cases of difficult diagnosis, an ultrasound of the inguinal region is performed. A safe and highly accurate instrumental method helps determine the type of protrusion, its size, stage, and the presence of strangulation.
When collecting the anamnesis, the doctor can ask parents clarifying questions to assess the child's risk status, which plays a significant role in an accurate diagnosis.
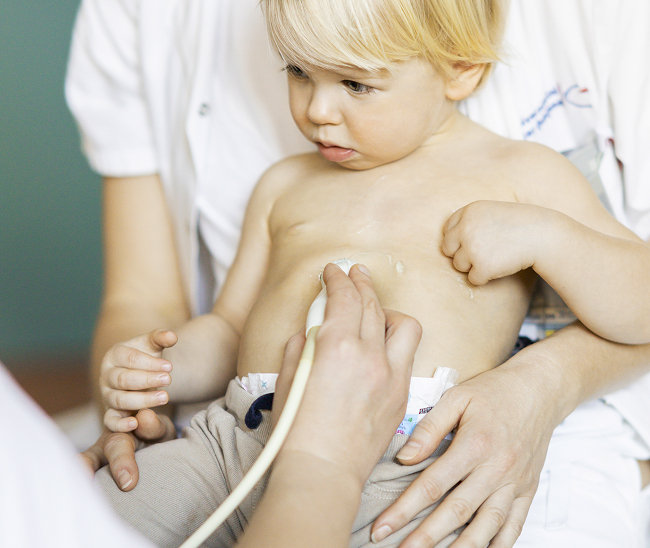
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis requires consideration of a number of conditions that may have similar manifestations but require a completely different approach to treatment. The main pathologies to rule out are:
- Hydrocele (hydrocele) is a fluid accumulation in the inguinal canal or scrotum without organ displacement.
- Epididymitis or orchitis are inflammation of the testicle or epididymis, accompanied by pain, redness, and fever.
- Inguinal lymphadenitis is enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes; When palpated, the nodes feel like dense structures, usually bilateral.
- Inguinal cyst or femoral canal hernia: Unlike an inguinal hernia, it is located below the inguinal ligament and requires a different treatment approach.
- Cryptorchidism (undescended testicle) - may be accompanied by a bulging or enlarged scrotum, but the testicle remains in the abdominal cavity or inguinal canal.
Methods for treating inguinal hernia in children
Therapy is aimed at removing the hernia and preventing complications. Depending on the child's age, the condition of the hernia, and the presence of complications, either conservative observation or surgery—the primary treatment for confirmed hernias—may be used.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment of inguinal hernias in children is used only in rare, strictly limited cases—for example, if the child is too young or there are contraindications for surgery. In such situations, close medical supervision is required. It is important to follow recommendations to limit weight bearing, avoid straining, and have regular checkups with the surgeon.
Surgical treatment
Surgery is the primary method for correcting inguinal hernias in children.
The surgery is usually performed under anesthesia, so the slightest discomfort is excluded.
Main types of interventions:
- Open hernia repair is a classic procedure that has been used in medical practice for many years. The surgeon makes an incision in the skin and soft tissue, isolates the hernia sac, returns the trapped organs to their original position, and sutures the hernia. The anterior abdominal wall is then strengthened using the patient's own tissue or a synthetic mesh.
- Laparoscopic hernia repair is performed through mini-incisions using a camera and instruments, which reduces postoperative scarring and speeds up recovery. During minimally invasive surgery, a laparoscope—a thin instrument with a camera that transmits images to a screen—is inserted into the abdominal cavity. Surgical instruments are inserted through additional punctures, and the doctor uses them to repair the hernia. Laparoscopic surgery is especially appropriate for bilateral hernias and recurrences, as well as when it is important to minimize cosmetic defects.
During surgery, the child's condition is closely monitored by an anesthesiologist. The patient is discharged only after a medical examination.
Inguinal hernia surgery is characterized by high safety and a good prognosis—the risk of recurrence and serious complications after a properly performed procedure is low.
In infants, surgery is performed only in emergency cases. Whenever possible, doctors try to postpone complex interventions until 6-12 months.
FAQ
We answer the most frequently asked questions about inguinal hernia treatment in children.
Is it possible to treat an inguinal hernia without surgery?
In children, inguinal hernias most often require surgical treatment. Conservative methods are used only as a temporary measure to monitor and maintain the patient's condition before more radical measures are taken.
What age is best for surgery?
Elective inguinal hernia surgery is possible as early as 6 months. If the condition is strangulated, surgery is performed immediately, regardless of age.
How safe is surgery on newborns?
Thanks to modern techniques, experienced surgeons, and gentle anesthesia, inguinal hernia surgery is safe and has a minimal risk of complications.
Is hospitalization necessary for inguinal hernia surgery?
Many surgeries are performed on an outpatient basis, and the child is sent home the same day. However, if the hernia is complicated or there are underlying medical conditions, the patient may require a hospital stay.
How long does recovery after surgery take?
Full recovery takes up to a month. To speed up the recovery process, it is necessary to limit physical activity and follow your doctor's recommendations to prevent recurrence.
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services








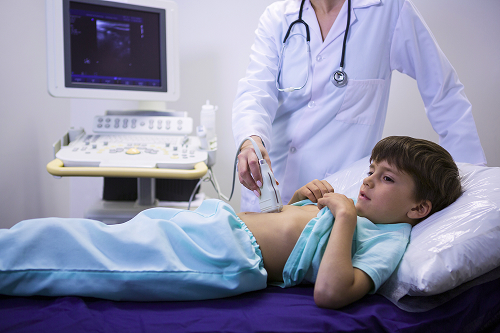

























































Definition and general information
Inguinal hernias are a common surgical condition. They are diagnosed in 1-3% of full-term newborns and 13-18% of full-term infants. Boys are affected up to 8 times more often than girls.
Inguinal hernias in children are predominantly congenital and are a localized manifestation of mesenchymal insufficiency syndrome. Understanding the anatomical features of the inguinal canal and the mechanisms of disease development plays an important role in timely diagnosis and the prescription of effective treatment.