Labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis is an inflammation of the inner ear. It develops as a result of the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms into the anatomical structures of the organ of hearing. Inflammation can also be caused by toxic waste products of bacteria and viruses. The disease manifests itself in the form of hearing impairment and body coordination in space.
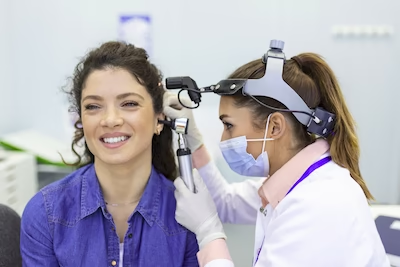
The disease is quite dangerous and requires mandatory treatment in a clinic. Self-therapy of labyrinthitis is ineffective, moreover, it can aggravate the inflammatory process. In the international center "Clinic K+31" treatment of ear diseases is carried out by qualified otolaryngologists with extensive experience of clinical work. We use the most modern medical equipment and the safest drugs.

specialists
equipment
treatment

Causes of the disease
Another name for the pathology is internal otitis. The direct cause of the painful process is the penetration of pathogenic bacterial or viral agents into the anatomical structures of the hearing organs. Inflammatory processes lead to hearing loss, cause dizziness and other unpleasant symptoms.
There are many factors that can provoke the development of internal otitis:
- Progress of otitis media - the movement of the inflammatory process inward
- Intracranial injuries
- Infectious lesions of the body
- Benign tumors localized in the area of the organs of hearing
- Acoustic trauma: sound overload, high-frequency sound directed directly into the ear canal
The most likely cause of labyrinthitis, as evidenced by medical statistics, is a complicated course of otitis media. Insufficient or inadequate treatment leads to the spread of inflammation deep into the ear. This form of the disease is called otogenic labyrinthitis. Often, labyrinthitis develops as a complication of infectious diseases of other localizations. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the inner ear hematogenously (through the blood).
Infectious diseases that provoke labyrinthitis are:
- Flu
- Mumps
- Syphilis
- Tuberculosis
These diseases are dangerous in themselves, and if they are also accompanied by inflammation of the inner ear, treatment becomes doubly difficult and lengthy. In such cases, complex therapy is carried out - the main pathology is eliminated, then local therapy of the inner ear is carried out.
When the disease develops, inflammation develops in the labyrinth - a structural element of the organ of hearing. This anatomical section performs not only the function of hearing, but is also responsible for the sense of balance. That is why during the disease patients experience dizziness and spatial orientation is impaired.
The labyrinth is localized in the area of the temporal bone and is adjacent to the tympanic cavity from the inside, and to the auditory canal from the outside. It consists of 3 parts - the cochlea, the vestibule, and the semicircular canals. When inflammation occurs, all components of the inner ear are affected, which causes quite characteristic symptoms.
The disease begins with tinnitus, loss of full orientation, dizziness. Hearing is reduced, and loud sounds cause painful reactions in the ear. Fluid (exudate) accumulates in the labyrinth. The most dangerous type is purulent labyrinthitis, which is accompanied by general intoxication of the body. With an unfavorable course of this form and the absence of timely and competent therapy, total hearing loss is possible.
Classification of labyrinthitis
There are several criteria for classifying the disease.
By the severity of symptoms
- Acute — this form of the disease is more common than others. Serous labyrinthitis occurs suddenly, but with timely and adequate therapy does not last longer than 2 weeks. This form is characterized by slight local redness of the ear canal and typical signs of inflammation - pain, burning in the ear. Conservative therapy, involving the use of internal and external medications. Acute purulent labyrinthitis is more dangerous and often requires radical treatment - surgery may be needed
- Chronic — the process is characterized by a protracted course and latent symptoms. The absence of pronounced signs does not mean that treatment can be omitted. The inflammatory process in chronic labyrinthitis continues and can at any time turn into an acute stage. Most often, recurrent labyrinthitis is a consequence of insufficient treatment of the acute form of the disease
By prevalence of the disease process
- Limited — localized in individual anatomical components of the inner ear and most often acts as a complication of otitis media. This type of pathology is usually accompanied by the formation of a fistula
- Widespread — diffuse or widespread labyrinthitis covers all elements of the bony labyrinth. In some situations, even bilateral internal otitis is diagnosed, in which pathological processes occur in both hearing organs at once
Symptoms of labyrinthitis

The most characteristic symptom of the disease in question is dizziness, often accompanied by nausea. The latter symptoms are associated with vestibular nerve stimulation.
Dizziness with labyrinthitis is expressed in the illusion of rotation of external objects or the patient himself. The head spins more when tilting the head, moving, sneezing and mechanical impact on the auricle. Dizziness is associated with pathological impact on the semicircular canals. With acute inflammation, dizziness occurs in attacks of varying duration. With recurrent labyrinthitis, dizziness is less pronounced.
Other symptoms of labyrinthitis in adults:
- Deterioration of spatial coordination, swaying when walking or falling to one side
- Hearing loss or complete loss of hearing in the affected ear
- Nystagmus - tremor of the eyeballs (not an obligatory symptom)
- Signs of general intoxication (with bacterial purulent labyrinthitis) - fever, headache, weakness
- Intense sweating (hyperhidrosis) - this manifestation occurs in the debut stage of the disease and is associated with excitation of the vagus nerve
- Change in heart rhythm - decreased heart rate
The severity of symptoms depends on the cause and type of disease. Acute purulent or necrotic otitis is the most dangerous and obvious pathological form. Often the disease develops in attacks. During critical periods, patients experience severe dizziness (up to the inability to move or move their head), their complexion changes, and their pulse slows down (or quickens).
With labyrinthitis caused by skull damage, an accumulation of exudate mixed with blood is often observed in the labyrinth. Injury to the temporal bone can cause paresis (temporary paralysis) of the facial nerve: the patient becomes unable to control the muscles of one half of the face.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services