Diseases of the pancreas
The pancreas is an unpaired glandular organ of the digestive system that produces pancreatic juice with a large number of enzymes. At the same time, it performs an endocrine function, producing the hormones insulin and glucagon. Dysfunctions of this organ often lead to the development of serious diseases of the pancreas, many of which are characterized by rapid, malignant progression.

specialists

equipment

treatment
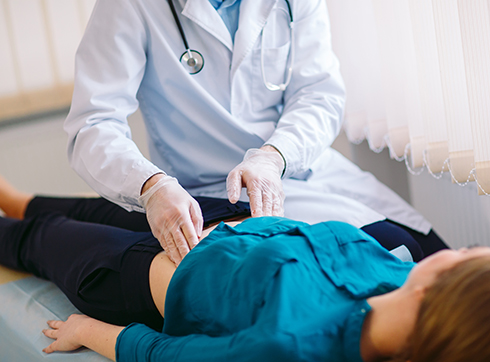
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory condition of the pancreas. It can be acute or chronic. The disease develops due to the following reasons:
- Abuse of alcohol and unhealthy heavy food
- Presence of stones in the gallbladder
- Metabolic disorders
- Uncontrolled use of antibiotics, antiviral drugs and chemotherapy drugs
The main symptom of acute pancreatitis is severe pain in the upper abdomen. Depending on the form and stage of pancreatitis, it can radiate to the back or chest.
Among the additional symptoms of pancreatitis, nausea and vomiting that do not bring relief, as well as fever and rapid heartbeat should be highlighted. With chronic inflammation of the pancreas, there is a deterioration in the general condition, accompanied by rapid weight loss and problems with stool.
Diagnosing pancreatitis
How to check the pancreas? Diagnosis begins with an analysis of the patient's symptoms and medical history. To measure the level of pancreatic enzymes, the doctor issues a referral for a laboratory test of blood and urine.
Such diagnostic methods as ultrasound, CT and MRI allow you to clarify the size and extent of damage to the organ.
Features of therapy
The treatment plan for the pancreas in pancreatitis depends on its form and severity. The stages of therapy for the acute type of the disease are as follows:
- Elimination of pain syndrome
- Diet (required to facilitate the work of the pancreas)
- Infusion therapy
- Use of antibiotics (if infection is suspected)
Therapy for chronic pancreatitis includes a therapeutic diet, taking analgesics and drugs that help replenish missing digestive enzymes. In case of severe organ damage, surgery is required (usually laparotomy or puncture-drainage intervention is prescribed).
If you contact a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis after treatment of pancreatitis is favorable. Otherwise, intestinal dysbacteriosis, diabetes mellitus or oncology develops. At the terminal stage of the disease, there is a risk of peritonitis.
Pancreatic cancer
Causes of the disease
The risk of developing cancer is increased in people with type 2 diabetes. Other provoking factors include:
- Excess weight (at risk are people with fat deposits in the abdominal area)
- Smoking
- Alcohol abuse
- Liver and gallbladder diseases (cirrhosis, cholelithiasis)
- Chronic pancreatitis
The risk group also includes men over 45 years old. This is due to bad habits and poor nutrition.
Symptoms of oncology
Signs of pancreatic cancer are often non-specific. That is why its timely detection is often complicated. Possible initial manifestations of the disease include:
- Pain syndrome (if the head is affected - under the right rib, tail - in the upper abdomen on the left. Girdle pain is observed with cancer of the entire organ), which decreases when lying on the back
- Gradual weight loss. Combined with nausea, vomiting and general weakness
When the tumor disintegrates, intoxication occurs. Against this background, specific symptoms appear - sudden weight loss, increased body temperature and aversion to meat. Ascites and bleeding are allowed.
Diagnostics
How to check the pancreas? The process of diagnosing cancer begins with an analysis of symptoms and a visual examination. Then the specialist sends the patient for laboratory tests and instrumental studies (ultrasound, CT, MRI). A biopsy is also required to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Features
How to treat the pancreas when cancer is detected? If there are no metastases, surgery is performed. The main types of surgical intervention:
- Whipple operation (pancreatoduodenectomy)
- Distal pancreatectomy
- Total pancreatectomy
- Nano-knife (used when the malignant neoplasm is inoperable)
After surgery, the patient must undergo chemotherapy and radiotherapy. At the same time, he is prescribed a special diet and constant intake of pancreatic enzymes in tablet form.
Treatment at the K+31 clinic in Moscow: advantages, admission conditions
Only qualified doctors with many years of practical experience work at the K+31 clinic in Moscow. They quickly identify pancreatic diseases and provide safe and effective treatment.
We offer:
- Individual approach to each patient
- Modern diagnostic and treatment methods
- Comfortable conditions for staying at the clinic
You can get an appointment with a doctor by appointment.
You can reserve a time for a visit on our website or by phone. To do this, you will need to provide your full name and contact phone number.
If you have any questions, please contact us by phone: +7 (499) 999-31-31.
The clinic administrator will promptly consult you and make an appointment at the most convenient time.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services
Reviews































Where is the pancreas located and how does it hurt
Where is the pancreas? This organ is located in the upper part of the abdominal cavity. It is directly adjacent to the stomach and the first section of the small intestine (duodenum). The pancreas has the shape of an elongated sheet and extends from the area of the spleen to the central part of the body, where it connects with the liver tissue.
One of the most common signs of pancreatic damage is pain in the upper abdomen. Radiating to the back or chest area, the pain syndrome can be sharp and dull, constant and paroxysmal. Sometimes it goes away on its own, but more often it disappears only after taking medication.