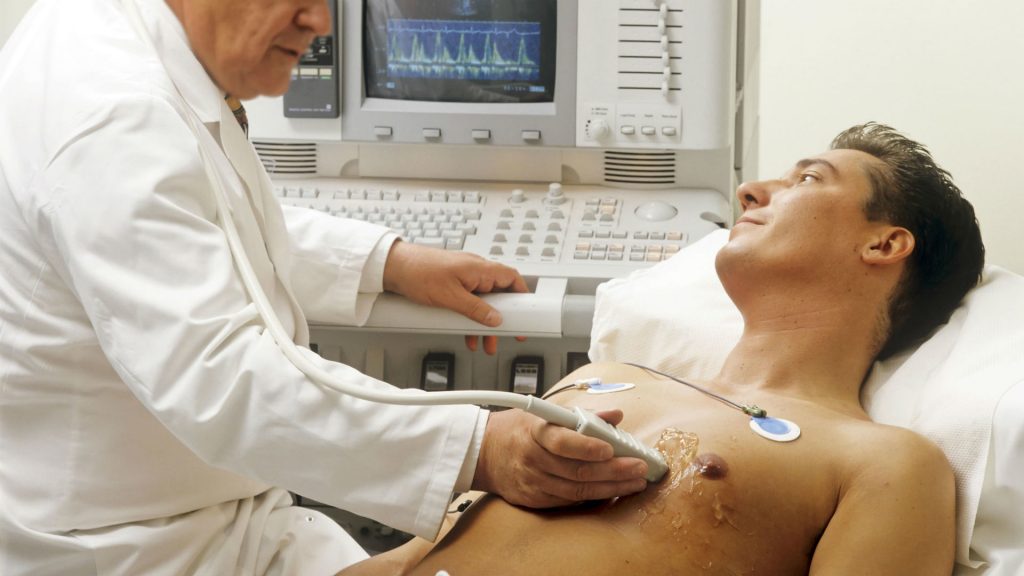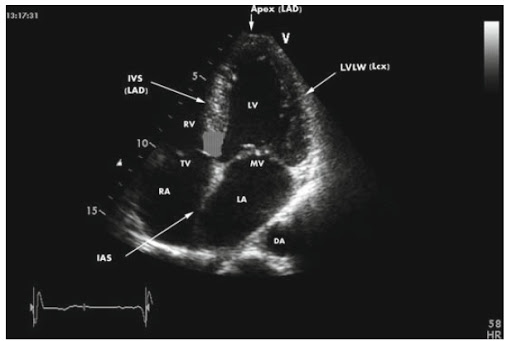
Indications for ECHO-KG
The principle of operation of the ECHO-KG is the same as for any ultrasound examination: the sensor sends ultrasound waves to the heart, which are reflected from the structures of the heart and return back to the sensor, after which they are analyzed and interpreted as an image on the monitor of the device.
How often does an ECHO-KG pass?
The frequency of the examination is determined by the doctor - cardiologist.
Dynamic examination of patients, on average 1 time per year, is recommended for patients:
- with heart diseases taking medications to evaluate their effectiveness;
- after cardiac surgery,
- with lesions of the heart valves (heart defects) to determine the need for timely cardiac surgery
- with expansion of the thoracic aorta
- with diseases of the heart muscle (myocardium), for example, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, myocarditis
- with ventricular or atrial septal defects
- professional athletes, pilots
A single examination is often necessary before planned surgical intervention in patients with a high risk of cardiovascular disease. There are no contraindications, there is no special preparation for the study, but the possibility of ultrasound examination may be limited due to the excess weight of the patient, the structure of the chest.
Echocardiography is indicated for patients with suspected heart disease or with already known heart disease, most often these are patients with:
- high blood pressure
- chest pain
- shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air
- heart rhythm disturbances, rapid / irregular / rare heartbeat
- fainting, dizziness
- prolonged fever (fever)
- swelling of the lower extremities
- ECG changes (electrocardiogram)
- with a heart murmur that the doctor determines when listening to the heart
- changes in the heart shadow on the chest radiograph
- burdened by heredity for cardiovascular disease
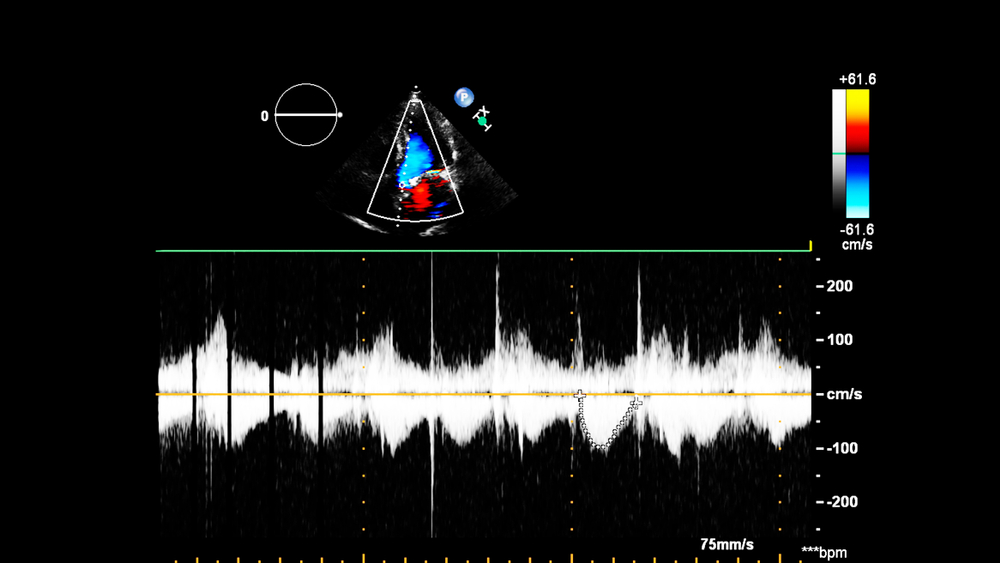
ECHO-KG is performed with the periodic appearance of edema on the legs in the late afternoon, in the case of frequent fainting, spikes in blood pressure, acrocyanosis (the dark color of the most distant points of the body: the tip of the nose, lips, fingertips, etc.).
Indication for ECHO-KG is the presence of heart murmurs, persistent rhythm disturbances, severe tonsillitis and bacterial infections of the kidneys, heart injuries, and a "bad" electrocardiogram.
What allows to detect ECHO-KG?
ECHO-KG measures heart parameters such as the volume of cavities, the thickness of the walls of the ventricles and atria, the area and diameter of the valves, the presence of blood regurgitation (current in the opposite direction with valve pathology), and the ejection fraction - all this plays a huge role in the diagnosis of heart diseases -vascular system. Also defined are:
- All kinds of congenital malformations of the heart: tetralogy of Fallot, open oval window, non-closure of the Botall duct, etc.
- Acquired malformations: stenosis and insufficiency of heart valves;
- Traces of active or transferred infections in the heart: endo-, myo- and pericarditis, chronic rheumatic heart disease;
- Myocardial sites with reduced contractile activity: areas of dys-, hypo- and akinesis that occur after myocardial infarction, severe myocarditis;
- The presence of blood clots inside the heart, which is characteristic of chronic arrhythmias;
- The state of the epicardium (external lining of the heart), pericardium (cardiac "shirt"), cardiac sac for the presence of fluid in it;
- The state of the initial sections of the aorta, for example, its stratification in the ascending part.
Difficulty performing ECHO-KG
ECHO-KG has no contraindications, however, in some cases, certain difficulties may arise during its implementation. In patients with a deformed chest, the normal anatomical location of the ribs, sternum and intercostal spaces is disrupted, which makes it difficult to visualize the heart from a standard position.
Bad signal can be obtained in women with large breast size.
Examination of the heart through the front wall of the chest may not be possible if there is an extensive wound.
In all of these cases, transesophageal ECHO-KG may be an alternative.
Advantages of ECHO-KG
The main advantages of ECHO-KG include the high diagnostic value of the method, absolute harmlessness to the body, the absence of the need for invasive intervention, the absence of unpleasant sensations (for transthoracic ECHO-KG), low cost in terms of price-informativeness.
Disadvantages ECHO-KG
The main disadvantage of ECHO-KG is the need for expensive equipment and the presence of a qualified specialist who knows how to use this equipment and interpret the data obtained in the conclusion we are familiar with.
ECHO-KG in the clinic K + 31
Clinic K + 31 is devoid of these shortcomings: our medical center has modern devices for conducting ultrasound examinations, including echocardiography. We focus on the health of patients and conduct all research on the latest equipment, minimizing the risk of a diagnostic error.
Also, the staff of our clinic has specialists who own the ECHO-KG equipment at the highest level. All this together allows us to accurately and accurately diagnose, prescribe the right treatment and maintain health for you.