Atherosclerosis Treatment
Atherosclerosis is currently one of four common diseases that cause premature disability and death. It most often affects people aged 40-45 and is three to four times more common in men.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Reasons
There are various risk factors for developing the disease - irremovable, removable, and partially removable.
Removable:
- Age
- Gender
- Heredity
Removable:
- Arterial hypertension
- Alimentary obesity
- Smoking
- Insufficient physical activity
- Excessive emotional stress
- Poor diet
Partially removable:
- Diabetes mellitus
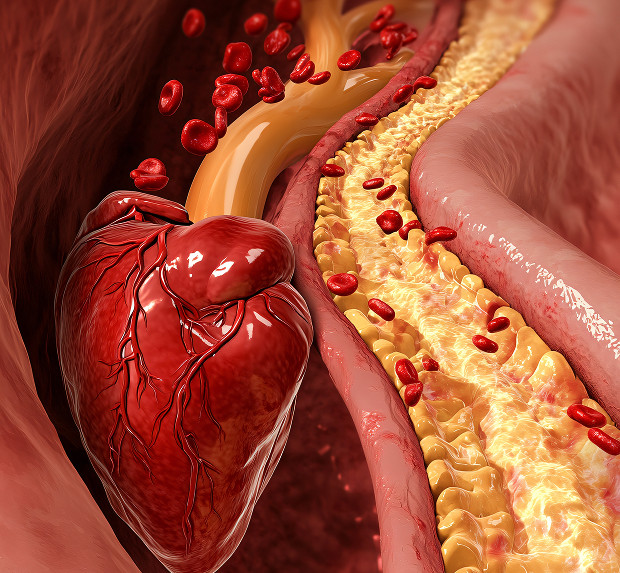
Cholesterol and Atherosclerosis
Cholesterol, a substance produced by our bodies and consumed through food, is closely linked to the development of atherosclerosis. Many important processes, including the construction of cell membranes and hormone production, are impossible without cholesterol. However, an excess of this substance can cause serious damage to the body.
High cholesterol is especially dangerous for our blood vessels. When this substance is elevated in the blood, low-density lipoprotein particles ("bad cholesterol") settle on the inner lining of arterial walls. Fats, calcium, and other substances gradually accumulate there, forming atherosclerotic plaques. These plaques grow slowly, narrowing the vessel lumen and impeding normal blood flow.
But not all cholesterol is equally harmful. There are also high-density lipoproteins ("good cholesterol"), whose job it is to cleanse the walls of blood vessels of excess fat. They help flush excess cholesterol back to the liver, preventing the formation of new plaques.
It's important to maintain balanced cholesterol levels in the body by monitoring diet and physical activity, and regularly testing your blood for both types of cholesterol.
Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis

The disease is characterized by a long development and unnoticeable initial stages. Atherosclerosis begins with damage to the inner layer of the arteries—the endothelium. The damaged area loses its smoothness and elasticity, becoming vulnerable to the penetration of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles.
LDL molecules are oxidized, turning into toxic compounds that can cause further changes in the vessel tissue. Cholesterol molecules entering the vessel wall attract the attention of macrophages, which engulf the oxidized LDL cholesterol, transforming into foam cells that exacerbate local inflammation.
The inflammatory process promotes the formation of a fibrous capsule around the lipid accumulation, which limits the growth of the arterial lumen. As the lipid content increases and the fibrous capsule grows, a stable atherosclerotic plaque forms. Its growth is accompanied by a decrease in vessel diameter and a decrease in blood flow velocity.
If an atherosclerotic plaque grows continuously and for a long time, it can lead to a number of serious complications, such as thrombosis or vascular occlusion. Chronic atherosclerosis often goes unnoticed by the patient until the first clinical symptoms appear. Regular examinations and preventative measures play a key role in maintaining cardiovascular health.
- Stage One: Formation of visible lipid deposits on the inner lining of the arteries (so-called "fatty streaks")
- Stage Two: Further deposition of lipids (fats and cholesterol) and the appearance of rounded, dense formations (atheromas) or atherosclerotic plaques protruding into the lumen of the vessel and narrowing it.
- Stage Three: Necrosis (damage) begins within the plaques. Progression of the process leads to plaque resolution, hemorrhage, and thrombus formation in the ulcerated areas. The ulcers can weaken the strength of the vessel walls, leading to the formation of aneurysms (especially in the aorta). Dense scars begin to form at the site of the ulcers, affecting the elasticity of the arterial walls, which is necessary to maintain normal blood pressure.
Classification of Atherosclerosis
For ease of diagnosis and treatment, a classification of atherosclerosis has been developed based on various characteristics, such as location:
- Coronary: affects the heart arteries, disrupting the blood supply to the heart muscle
- Cerebral: affects the vessels of the head and neck, affecting cerebral circulation
- Peripheral: affects the arteries of the legs and arms, impairing blood flow to the extremities
Classification of Atherosclerosis by Stage:
- Initial: the first small asymptomatic Plaques
- Moderate: arterial lumen significantly narrows, and the first unpleasant sensations begin.
- Late: severe narrowing of blood vessels or complete vascular blockage. Serious problems develop at this stage.
By course of the disease:
- Slowly progressive atherosclerosis: develops gradually, is asymptomatic.
- Rapidly progressive atherosclerosis: the disease actively gains momentum, rapidly deteriorating health.
Knowledge of the classification helps doctors more accurately assess the situation and choose the appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is insidious because it can develop latently for a long time, showing no signs. But when plaques become large enough, characteristic symptoms develop, depending on the specific vessels affected.
Early signs often go unnoticed, as many people assume that weakness, headaches, or slight numbness in the extremities are temporary, caused by fatigue or stress. Therefore, it's important to listen to your body and consult a doctor promptly if suspicious symptoms arise.
The main manifestations of the disease include:
- A feeling of chest pain similar to angina attacks. The heart suffers from oxygen deprivation because the coronary arteries are clogged with cholesterol deposits
- Frequent headaches, dizziness, and memory and concentration impairment are caused by poor blood circulation in the cerebral vessels. Sometimes patients report sudden mood swings, irritability, and fatigue
- Problems with legs and arms. If the blood vessels in the lower or upper extremities are affected, a feeling of heaviness, pain, and numbness in the legs or arms occurs when moving. Walking becomes a torturous task; the legs are constantly cold, and the skin becomes pale and dry
Subsections by Location
Coronary Arteries
When atherosclerosis affects the heart vessels, it is called coronary atherosclerosis. This causes problems with blood supply to the heart, leading to symptoms such as:
- Attacks of chest pain (angina)
- A feeling of tightness or discomfort in the chest
- Shortness of breath, fatigue
Damage to the coronary arteries can result in myocardial infarction—the death of sections of the heart muscle due to complete blockage of the artery. This is one of the most serious complications and requires immediate medical attention.
Brain
If atherosclerosis spreads to the blood vessels of the brain, it is called cerebral atherosclerosis. This situation can disrupt blood flow to the brain, causing the following symptoms:
- Dizziness, tinnitus
- Memory impairment, difficulty concentrating
- Slurred speech, lapses in consciousness
- Nausea, general weakness
The most severe consequence is a stroke, caused by a complete interruption of blood flow to some part of the brain. A stroke can lead to paralysis, sensory loss, or other serious consequences.
Lower Extremities
Atherosclerosis of the leg vessels causes poor blood flow to the muscles and skin, leading to symptoms such as:
- Leg pain that occurs only when walking—this condition is called intermittent claudication
- Cramps, heaviness in the legs
- Cold feet, skin discoloration (cyanosis)
- Delayed wound healing, foot ulcers
The most serious complication of lower extremity vessels is gangrene, when tissues stop receiving sufficient oxygen and begin to die. This may require surgical intervention, including amputation.
Renal Artery
Renal artery atherosclerosis impairs kidney function, interfering with urine production and fluid control. Typical symptoms of this disease include:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Swelling of the face and legs
- Problems with urination
- Fatigue and weakness
If left untreated, this type of atherosclerosis, damage to the artery that carries blood to the kidneys, can lead to chronic kidney failure, when these two organs lose their ability to function properly.
Each case of atherosclerosis is unique, but understanding the characteristics of its different forms allows for faster recognition and proper treatment.
Disease prognosis
Atherosclerosis is a disease that cannot be completely cured, but it can be successfully managed. The prognosis depends on the extent of vascular damage, the presence of comorbidities, the patient's willingness to make lifestyle changes, etc.
Early diagnosis and adequate treatment help slow the progression of the disease. Modern medications effectively lower cholesterol levels, stabilize blood pressure, and protect blood vessels from further damage. A proper diet, physical activity, and avoiding unhealthy habits complement drug therapy, maintaining cardiovascular health.
Left untreated, atherosclerosis becomes chronic and continues to progress, increasing the risk of serious complications. Advanced atherosclerosis significantly reduces life expectancy.

Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to completely cure atherosclerosis?
When is surgery necessary?
How to lower cholesterol without medication?

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price






























































What is atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease in which fatty deposits (plaques) form within the walls of large blood vessels. This condition most often affects large arteries: the carotid, coronary, renal, and peripheral.
The resulting plaques gradually narrow the lumen of the vessel, impeding normal blood flow. The greater the narrowing, the more severely the blood supply to the body's organs and tissues is disrupted. When blood flow is severely restricted, organs begin to experience oxygen starvation, leading to serious complications.
Atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries is especially dangerous. If the coronary arteries are severely blocked, there is a risk of myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries can lead to stroke, as the brain's oxygen supply is severely reduced.
The disease can lead to disability or even death. Under no circumstances should the seriousness of this health-threatening and life-threatening condition be underestimated and timely diagnosis and treatment should be delayed.