Diagnostics
It is often possible to recognize angina pectoris at the first treatment of the patient, since complaints and a detailed history often compose a typical clinical picture.
Early detection of the clinical picture of angina pectoris can prevent such formidable complications as acute myocardial infarction, sudden cardiac death.
Most patients have a stable course of the disease - pain attacks of similar duration and strength that occur with a certain regularity in response to the load, stopping at the end of the load or when taking nitroglycerin.
Laboratory diagnostics
If an elevated level of cardiospecific enzymes is detected in a biochemical blood test, urgent hospitalization of the patient is necessary. Most often, an increased level of biomarkers of myocardial damage indicates the presence of acute coronary syndrome (progressive angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction).
Instrumental diagnostics
- ECG at rest. Most often, indicators recorded at rest will be within normal limits. However, some patients may show signs of coronary heart disease (for example, history of myocardial infarction or impaired repolarization), as well as other changes (left ventricular hypertrophy, various types of arrhythmias). This allows you to determine the further plan of examination and treatment. An ECG is much more informative if it is recorded during an attack of angina pectoris (ECG dynamics occur that disappear outside the attack);
- ECG with physical activity. Apply treadmill test or bicycle ergometry with ECG monitoring. The main diagnostic criterion for ECG changes during such tests: horizontal or oblique depression of the ST segment ≥0.1 mV, persisting for at least 0.06-0.08 s, in two or more ECG leads. The use of stress tests is limited in patients with an initially altered ECG (for example, with blockade of the left bundle branch block, arrhythmias, or WPW syndrome);
- daily ambulatory ECG monitoring (Holter monitoring). This method is less informative than stress tests, but it can detect myocardial ischemia during normal daily activities, and also helps diagnose vasospastic angina pectoris;
- resting echocardiography - allows you to assess the condition of the myocardium, the safety of the valvular apparatus of the heart, its contractile activity and identify areas of contractility reduction;
- stress echocardiography. It allows you to evaluate the functional ability of the myocardium under load, to identify transient zones of reduced myocardial contractility. Perform echocardiography in combination with pharmacological or physical activity;
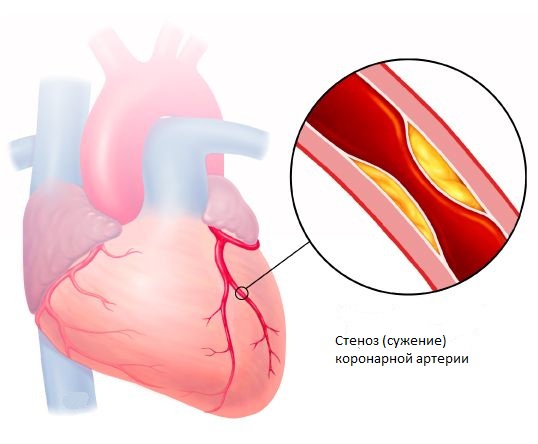
- CT coronary angiography - contrasting of the coronary arteries with the detection of atherosclerotic plaques stenosing the lumen of the coronary arteries.
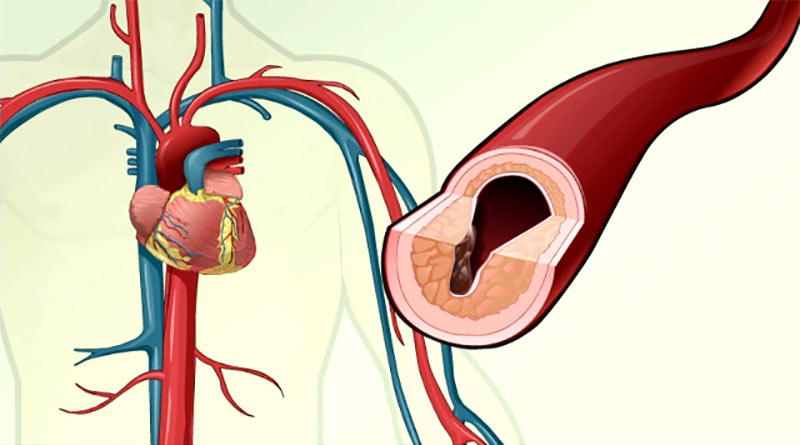
Angina treatment
The goal of treating angina pectoris is to prevent the progression of the disease (the development of myocardial infarction) and the elimination of clinical symptoms.
In the clinic "Clinic K + 31", doctors carry out drug treatment.
With the ineffectiveness of drug therapy, as well as in the presence of a high risk of complications, surgical treatment is usually performed. Balloon angioplasty and stenting of the coronary arteries are performed in the presence of 1-3 stenoses (detected by CT-coronarography), or coronary artery bypass grafting in the presence of 4 or more stenoses, or stenosis of the left coronary artery trunk.