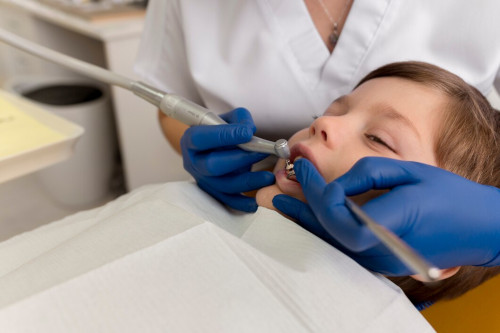
Treatment of primary and molar teeth

specialists

equipment

treatment

Causes of dental diseases in children
- Poor oral hygiene
- Prolonged use of a nipple on a bottle, especially when the baby falls asleep with it in his mouth
- Transmission of pathogens from parents to children, for example, when using shared utensils
- Genetic predisposition to diseases of teeth and gums
- Excessive consumption of sweets and drinks
- Insufficient intake of calcium and fluoride from food
Prevention of dental diseases

To prevent caries in children, it is recommended to breastfeed until the age of one, daily brushing of teeth, and limiting the consumption of sweets until the age of three. It is also important to visit the pediatric dentist 1-2 times a year.
To strengthen your teeth, it is recommended to add dairy products to your diet. They contain calcium, which is beneficial for tooth enamel. It is also worth including vegetables, fruits and fish in the menu. They contain magnesium, phosphorus, fluorine and many vitamins that are important for the prevention of periodontal disease.
The use of anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
The use of anesthesia and sedation in the treatment of primary teeth in children is often justified and even recommended. It is important to understand the difference between these methods:
- Sedation helps calm the child and reduce anxiety before the procedure. For this purpose, doctors use safe means, for example, nitrous oxide. It does not anesthetize, but only relaxes the baby
- Anesthesia. Involves complete immersion of the child in sleep during treatment. For this purpose, drugs such as sevoran (through a breathing mask) and propofol (intravenously) are used. They do not have a negative effect on the child’s nervous system
Treatment of children's teeth under anesthesia is recommended in the following cases:
- Difficulties in establishing contact between the doctor and the child
- The child has a strong fear of dental procedures
- Upcoming complex or multiple interventions, for example, removal of several teeth or treatment of deep caries
For preschoolers and primary schoolchildren, staying in a dental chair for a long time can be difficult. Pediatric dentistry with anesthesia allows you to carry out the necessary procedures without discomfort and pain.
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other Services























































Why is it important to treat baby teeth?
Treatment of baby teeth should begin as soon as they appear. At an early age, when children consume little sweets, the risk of developing caries is low. At 3-5 years of age, the amount of sugar consumed increases, and oral hygiene is often not maintained properly, so the likelihood of dental problems increases.
At the age of 5-6 years, the replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones begins. This process is usually completed by age 14. If baby teeth are not treated, caries and other diseases can lead to their early loss and even harm future permanent teeth. In addition, if left untreated, difficulties arise in diction and chewing food, and the digestion process is disrupted.