Treatment of caries of primary and permanent teeth

specialists

equipment

treatment
How to identify caries

Caries on children's teeth can be detected during a routine visit to the dentist. At an early stage, the disease manifests itself as a small white spot on the surface of the tooth. As the disease progresses, a brown cavity forms on the tooth, in which food debris accumulates. If tooth decay is left untreated, it results in bad breath and a coating on the tongue.
Children over three years old often complain of toothache associated with caries. It may worsen after eating sweet, sour or hot foods. If the nerves in baby teeth become inflamed and acute pain occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Negative consequences of caries of primary teeth in children
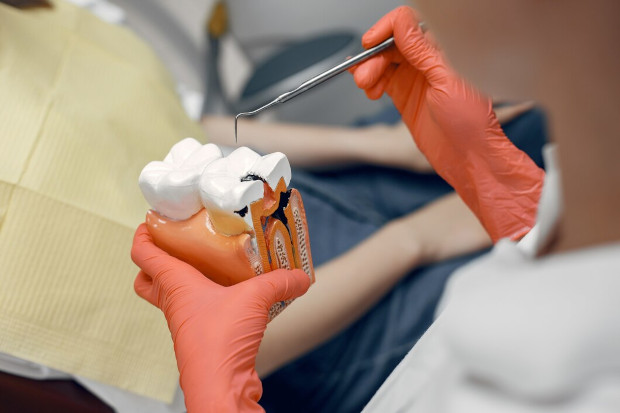
Caries in children threatens the development of serious complications. The most common is dental pulpitis (inflammation of the tissues inside the tooth), which can develop within 3-4 months after the onset of caries. In children under three years of age, the front teeth are usually affected; in older children, the chewing teeth are affected. Acute pulpitis causes severe pain, fever and refusal to eat, while chronic pulpitis has less severe symptoms. It often develops under fillings or in teeth heavily damaged by caries.
The second unpleasant complication is periodontitis or inflammation of the tissue around the tooth root. In children, acute periodontitis quickly worsens the general condition, causing severe pain, especially when eating hot food or pressing on the tooth. The child's temperature can rise to 39 degrees. Chronic periodontitis is less painful, manifests itself mainly during chewing, and is accompanied by swelling and redness of the gums near the affected tooth.
Types of caries of primary and permanent teeth in children
In addition to these types, there is bottle caries, which usually affects baby teeth in young children. This type of tooth decay develops due to frequent and prolonged contact of teeth with sugar-sweetened drinks during bottle feeding, especially during sleep. Bottle caries progresses quickly and can lead to serious tooth decay.
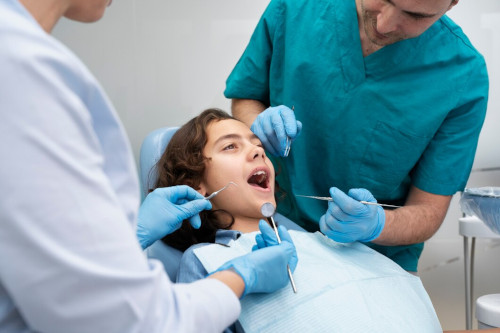
Depending on the location, there are three main types of caries in children:
- Fissure It develops in the grooves and recesses of the chewing surface of the teeth, where food accumulates and favorable conditions are created for the growth of bacteria. It is most often found on molars and premolars
- Approximal Occurs in the interdental spaces where brushing with a toothbrush is difficult. It often goes unnoticed until it affects the deeper layers of the tooth
- Cervical caries Appears in the neck of the tooth, where the enamel comes into contact with the gum. Often associated with poor oral hygiene and gum recession
General information about the procedure

Modern methods of diagnostics and dental treatment at "K+31"
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other Services




















































Causes of caries on children's teeth
Baby teeth are more vulnerable to caries than permanent teeth. This is due to thin enamel and wide dentinal canals. The immaturity of the child’s immune system also contributes to the rapid spread of pathology.
Factors that provoke the development of caries include:
Caries in children is common. Already at 1.5 years old, 10% of children are affected by at least one tooth, and by five years this figure increases to 70%. The main reasons are changes in eating habits and active communication with other children, which increases the risk of the spread of cariogenic bacteria. From the age of three, children begin to care for their teeth on their own, but often do not do it carefully enough.