Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a method that allows an optical video system to be inserted into the joint through a special "puncture" and to examine it completely. Arthroscopy provides an accurate diagnosis, makes it possible to see damage to the meniscus and ligaments, and identify the true cause of pain. And this is often difficult to establish not only with a conventional, but also with magnetic resonance imaging.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Advantages of joint arthroscopy
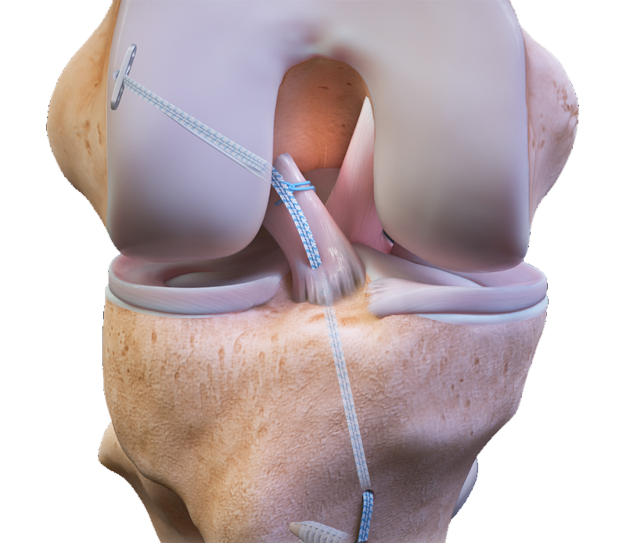
Minimal invasiveness of the operation. For example, most often for arthroscopy of the knee joint, anterior internal and anterior external approaches are used on the sides of the patellar ligament with dimensions of 3-5 mm for optics and arthroscopic instruments. These approaches make it possible to examine almost all parts of the joint and eliminate most intra-articular problems. A complete diagnosis of knee joint pathology is approaching 100%.
Arthroscopy of the knee joint helps to examine almost all parts of the joint and assess the functional state of the joint without compromising its anatomical integrity. Joint arthroscopy does not require long-term rehabilitation. After the operation, early weight-bearing on the limb is possible, walking without additional support is possible after 1-3 days, the period of disability is reduced from 4-6 weeks to 2-3 weeks. Such results are especially important for young people and professional athletes, since it becomes possible to start training as soon as possible and compete in competitions in a very short period of time. Reducing hospital stay for arthroscopy of any large joint. Discharge from the hospital after joint arthroscopy occurs within 1-3 days after the operation.
Indications for knee arthroscopy
At Clinic+31, knee arthroscopy is prescribed in the following cases:
- Damage to the menisci. The modern equipment of the orthopedics-traumatology department of Clinic+31 and the qualifications of our specialists allow us to perform not only resection of the damaged meniscus, but, if indicated, also its suture.
- Injury to the cruciate ligaments of the knee
- Inflammatory diseases of the synovial membrane
- Habitual luxation of the patella
- Inflammatory diseases of the synovial membrane
- Damage and disease of articular cartilage
- Deforming arthrosis of the knee joint
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Hoff's disease: damage and disease of the fat body - chronic hyperplasia of the fat body
- Unclear pathologies due to damage or disease of the joints, the causes of which have not been identified using clinical and instrumental research methods
- Unclear complaints after previously performed surgical interventions
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Reviews







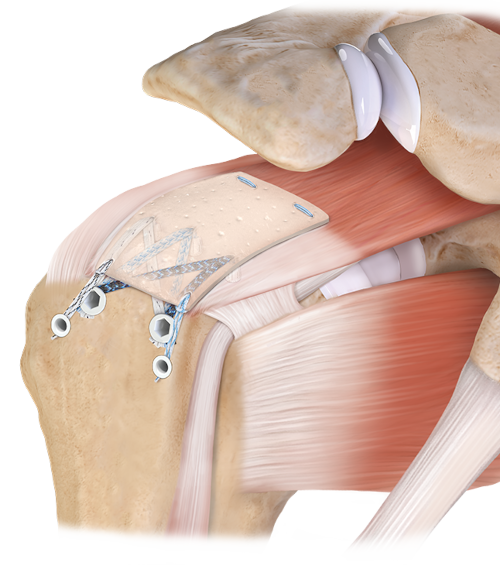
















































Advantages of joint arthroscopy