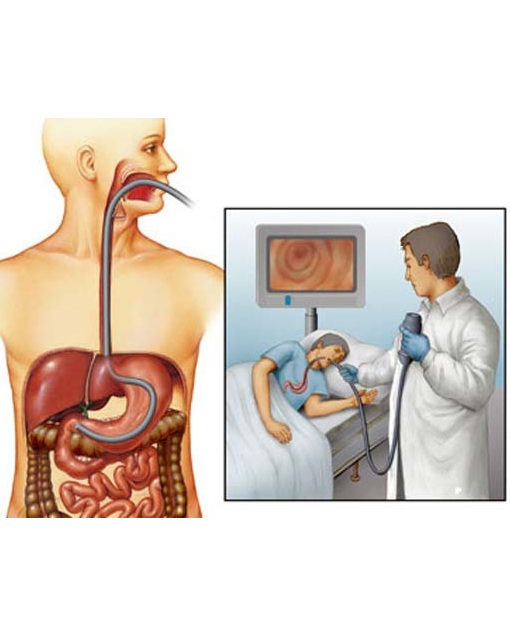
About the service
EGD is an endoscopic method for examining the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy can detect inflammatory foci, benign and malignant tumors, as well as any other pathological changes even in the early stages.
The results obtained by specialists after this procedure allow them to effectively diagnose gastrointestinal diseases. Other methods cannot boast the same high information content. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is performed using a gastroscope.
Types of esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure. EGDS is used to diagnose:
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Gastritis
- Benign and malignant neoplasms
- Intravenous bleeding
- Gastric polyps
- Varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach
- With the collection of biological material for subsequent laboratory testing for Helicobacter pylori
- With a biopsy for histological examination, etc.
Therapeutic EGDS is used when certain pathological changes are detected after diagnostics. In this case, esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a method of minimally invasive surgery that does not involve incisions or punctures. Thanks to this procedure, specialists perform the following therapeutic manipulations:
- Remove benign neoplasms
- Stop ulcer bleeding
- Remove polyps and ligature sutures
- Eliminate varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach
- Remove foreign bodies
- Perform endoscopic dissection, etc.
Indications and contraindications
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is performed if the patient has the following complaints:
- Stool disorders (black or tarry)
- Unpleasant sensations when swallowing
- Severe weight loss without reason
- Frequent nausea and vomiting
- Anemia of unclear origin
- Negative colonoscopy tests
- Signs of bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract
- Frequent heartburn
- Abdominal pain
- Lack of appetite or feeling hungry even after eating
- Chemical burns of internal organs
EGD is also necessary as part of cancer screening, examination after treatment for cancer or diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract, with esophageal stenosis.
Contraindications to the procedure
Despite the fact that esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a virtually harmless procedure, it is still invasive. In this regard, it also has contraindications. Most of them are relative, i.e. diagnostics will need to be postponed until the symptoms subside. Among them:
- Severe respiratory and cardiac failure
- Aortic aneurysm
- Acute mental disorders
- Blood clotting disorder
- Myocardial infarction or stroke
- Arrhythmia
- General severe condition of the patient
At the K+31 clinic, before prescribing EGDS, specialists necessarily conduct a detailed survey and examination of the patient, which also includes various diagnostic tests. This is necessary to completely exclude possible contraindications.
Rules for preparing for EGDS
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy can only be performed after it has been prescribed by the attending physician. The specialist explains the rules of conduct during the procedure and its purpose, and explains how to prepare for it. The possibility of performing EGDS under sedation is discussed. It may be necessary to eliminate existing worries. In this case, an additional consultation with an anesthesiologist is prescribed.
Some patients are also advised to temporarily stop taking certain medications (painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs) and adhere to a certain diet (exclude heavy foods). Taking special medications or performing an enema is not required.
General preparation rules include the following:
- Do not eat anything for 6-8 hours. Do not drink liquids for 4-6 hours
- Do not smoke or chew gum for several hours before the procedure
- Schedule the esophagogastroduodenoscopy for a day off
- Empty your bladder immediately esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is performed on an outpatient basis in a room specially equipped for endoscopic examinations. Before the procedure, a specialist may administer a mild sedative to the patient to relieve anxiety.
- The doctor anesthetizes the patient's oral mucosa and throat.
- The patient lies on his left side and clamps a special mouthpiece with his teeth. This is necessary to protect the teeth and endoscope from biting.
- If the patient undergoes diagnostics without sedation, the specialist asks him to inhale and swallow. At this time, the gastroscope is inserted into the body through the mouth. You need to breathe through your nose
- A gastroscope equipped with a backlight and a video camera passes from the esophagus to the stomach and duodenum. The entire process takes about 10-20 minutes. If necessary, additional biological materials are taken for subsequent studies or therapeutic manipulations are performed
Possible complications
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a safe procedure. But still, after its implementation, certain complications and risks are possible. They are related to the procedure of inserting the endoscope into the body and performing diagnostic and therapeutic manipulations:
- Painful sensations in the throat due to irritation
- Bloating
- Perforation in the stomach, esophagus or duodenum
- Bleeding at the biopsy site
You should immediately consult a doctor if, after undergoing EGDS, the patient experiences fever, vomiting with blood, or a change in stool that may indicate internal bleeding.
Specialists at the K+31 medical center perform esophagogastroduodenoscopy using modern equipment and in strict accordance with established rules. This allows you to minimize the risk of possible complications and obtain informative results.

Registration for a consultation
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.























