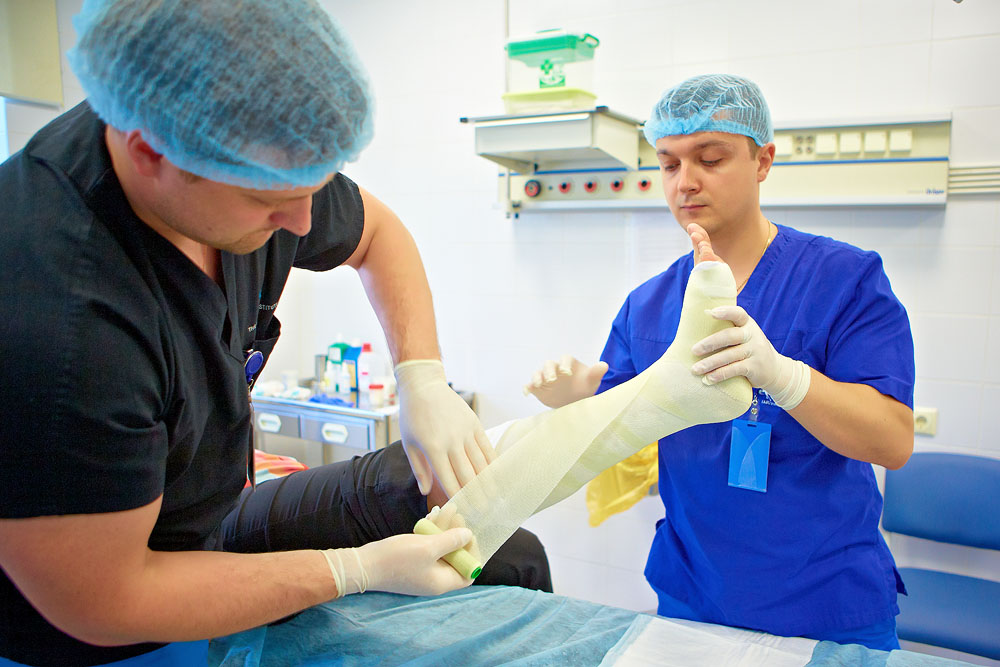
The health of the musculoskeletal system and the ability to move freely are the most important aspects of any person's life. And this is especially true for athletes, whose injuries occur much more often. Every day they endure increased physical activity, which negatively affects bones and joints, causing them to prematurely wear out. Sports injuries account for 5% of the total number of injuries. And we are talking not only about the activities of professional athletes, because anyone can get injured while skiing or even just playing tennis. In this case, it is necessary to urgently contact an orthopedic traumatologist who will carry out all the necessary diagnostic procedures and prescribe the correct treatment for the consequences of injuries.
Diagnostic examination
Before treating any injury, a number of diagnostic procedures are required. Their number and direction will depend on the size and location of the damaged area. The orthopedist-traumatologist can refer the patient to the following types of diagnostics:
- X-ray - is necessary to detect bone fractures;
- magnetic resonance imaging - shows in detail damage to bones, soft tissues, cartilage, nerves and blood vessels, usually performed with head or trunk injuries;
- densitometry is a non-invasive method for determining bone mineral density;
- computed tomography - the procedure is similar to MRI, but is performed using radiography;
- ultrasound - used for joint injuries.
Regardless of the complexity of the injury, the patient must pass urine and blood for biochemical analysis. This can be done after the provision of primary care. For example, for fractures, an X-ray is first taken and a plaster cast is applied.
The diagnosis also includes an examination by an orthopedist-traumatologist and narrow-profile specialists.










































