Heart rhythm disturbances are based on changes in the conditions of formation of excitation of the heart muscle or anomalies of its propagation paths. Arrhythmias can be caused by both functional disorders and severe organic lesions of the heart. In some cases, the cause of heart rhythm disturbances are congenital features of the cardiac conduction system. The state of the nervous system plays a certain role in the occurrence of arrhythmia. For example, mental and emotional stress causes changes in the rate, and often in the rhythm of heart contractions, including in healthy people. Arrhythmia often occurs in people with diseases of the central and autonomic nervous system.
Various diseases accompanied by disruption of the anatomical structure of the heart or metabolic processes occurring in it cause different types of arrhythmia in duration and nature, and only a doctor can establish a diagnosis, whose conclusions are based on clinical and electrocardiographic data.
Symptoms of arrhythmia
Quite often, patients do not feel the presence of arrhythmia. In these cases, arrhythmia is detected during a routine medical examination. However, many patients experience various sensations in the chest, which most often include:
- feeling of heartbeat and interruptions in the chest;
- very rapid heartbeat;
- extremely slow heartbeat (heart stopping);
- chest pain;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness or a feeling close to fainting.
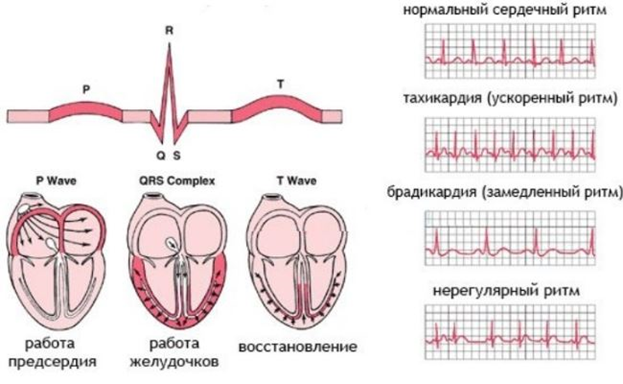
Classification of arrhythmias
1. Disturbances of automatism:
a) nomotopic (the pacemaker is in the sinus node):
- sinus tachycardia;
- sinus bradycardia;
- sinus arrhythmia;
- sick sinus syndrome (SSNS).
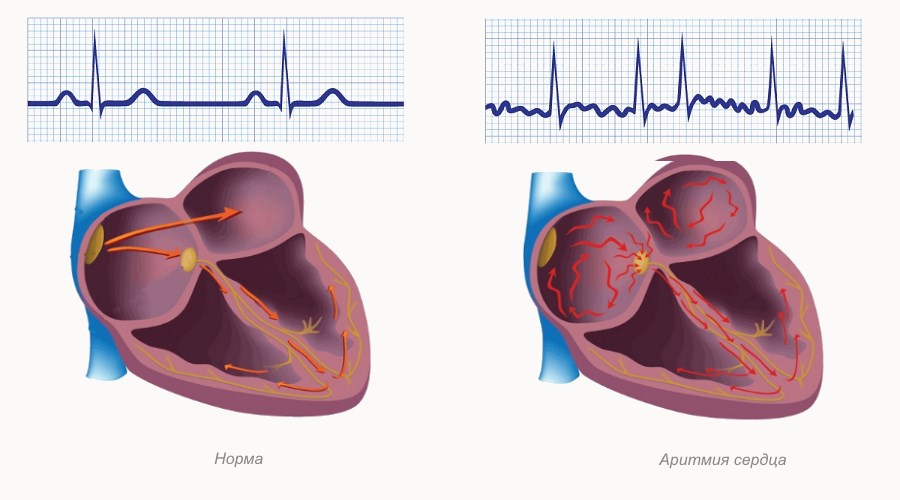
b) heterotopic (pacemaker is outside the sinus node):
- low atrial rhythm;
- atrioventricular rhythm;
- idioventricular rhythm.
2. Disturbances of excitability:
a) extrasystoles:
- by source: atrial, atrioventricular, ventricular;
- by the number of sources: monotopic, polytopic;
- by time of occurrence: early, interpolated, late;
- by frequency: single (up to 5 per minute), multiple (more than 5 per minute), paired, grouped;
- by order: disordered, allorhythmia (bigeminy, trigeminy, quadrigeminy).
b) paroxysmal tachycardia (atrial, AV, ventricular)
3. Conduction disorders:
a) increased conductivity (WPW syndrome);
b) decreased conductivity (blockades: sinoauricular, intra-atrial, AV, bundle branch block).
4. Mixed (atrial flutter/fibrillation, ventricular fibrillation)
Diagnostics
ECG is the main method for diagnosing arrhythmias. However, it is not always possible to detect arrhythmia when taking a resting ECG. In such cases, the K+31 clinic conducts daily ECG monitoring (Holter monitoring). Some arrhythmias are provoked by physical exertion, in which case stress tests (treadmill) are used to diagnose them.
Complications
A number of rhythm disturbances can lead to the development of serious complications. With an abnormal rhythm of contractions in the heart, blood flow slows down, which leads to the formation of blood clots in the atria. In the absence of adequate therapy, these blood clots can be carried with the blood flow throughout the body, leading to blockage of the arteries of the brain (stroke), arteries of the intestines, and lower extremities. Long-term existence of uncorrectable arrhythmia often leads to the development of heart failure.
Treatment of arrhythmias
- if arrhythmia is a consequence of some disease (for example, thyrotoxicosis), our doctors treat the underlying disease;
- antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed (affecting the cardiac conduction system, as well as various ion channels).
To prevent the development of complications, dynamic monitoring of the patient by a cardiologist is recommended even during the period of remission.