Causes
Symptoms of the presence of sulfuric plug
Diagnostics | Sulfur plug treatment
Prevention of the formation of sulfur plugs
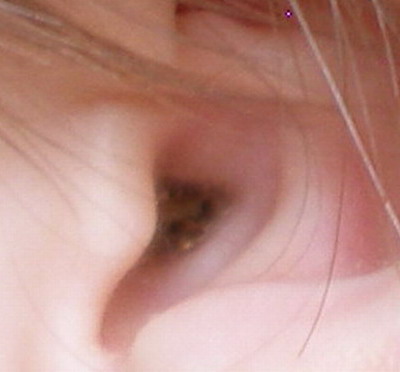
In the external auditory canal, in the thickness of the skin, there are special glands (cerumin) necessary for the secretion of a specific substance - earwax. The main function of this secret is protective, which includes antibacterial, antiviral and mechanical mechanisms. In the latter case, earwax, due to its sticky property, traps dust, preventing their deeper penetration.
Earwax is constantly produced in the external auditory canal, and its surface layer, contaminated with dust, microbes and other particles, gradually dries up and, together with the scales of the skin epidermis, falls out. The process of ear self-cleaning from "spent" sulfur is also facilitated by passive vibrations of the cartilage of the external auditory canal during movement in the lower jaw (chewing, talking, yawning).
If the natural process of removing sulfur is difficult, then sulfur plugs appear. They also form due to improper ear hygiene.
Thus, a sulfur plug is a blockage of the external auditory canal with a mass consisting of dry earwax, desquamated epithelium and dust particles.
You can diagnose and treat sulfur plug in the Department of Otorhinolaryngology K + 31.
Causes
The presence of sulfur plugs in the ears is a fairly common phenomenon, and a large number of reasons contribute to this:
- Improper hygiene of the outer ear, which consists in the use of cotton ear swabs and pushing the wax deep into the external auditory canal;
- Increased secretion of earwax due to too frequent removal of it;
- Metabolic disorders and especially cholesterol can stimulate the production of sulfur;
- Work in conditions of high dust content in the air (construction dust, flour);
- High humidity in the room or frequent ingress of water into the ear contributes to the swelling of sulfur and blockage of the ear canal;
- Too dry air makes it difficult to spontaneously remove sulfur and leads to its compaction and the appearance of a plug.
The formation of a sulfur plug is observed when the natural evacuation of sulfur is disturbed due to the pathology of the temporomandibular joint, narrowing or curvature of the external auditory canal.
Symptoms of the presence of sulfuric plug
Most often, sulfur plugs in the ears form for a long time . At the very beginning of its occurrence, no subjective sensations are noted, and only when the ear canal is blocked by more than 50%, the first symptoms appear in the form of congestion in the ear and hearing loss.
As the plug increases, these symptoms become more pronounced. Complete blockage of the external auditory canal significantly impairs hearing from the corresponding side. In addition, the pressure on the eardrum changes, resulting in:
- Tinnitus;
- Reflection (resonance) of your own voice in the ear;
- Vestibular disorders (dizziness, imbalance);
- Neuralgia (dull ear pain, headache);
- Emotional and mental disorders.
With prolonged presence of sulfur plug, the likelihood of inflammatory processes in the external (external otitis media) and middle ear (chronic otitis media) increases.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics of the sulfur plug is quite simple. To do this, you need to contact an otorhinolaryngologist, who will determine the pathology with a simple otoscopy. During the examination, the external auditory canal is examined using a special ear funnel. The presence of cerumen is indicated by a yellow or brown mass that completely covers the ear canal and eardrum. Large running sulfur plugs can be seen with the naked eye.
Diagnostic assistance is provided by the patient's characteristic complaints, the study of ear hygiene, information about past illnesses and laboratory tests.
Sulfur plug treatment
Wax plug removal should only be done under the guidance of an experienced otorhinolaryngologist.
Old-timers of the first medical institute remember the case when a sulfur plug was given by the entire staff of the clinic for two weeks! Almost all employees, from interns and subordinates to the head of the department, put their hands on it. As a result, the plug was removed. The name of the winner has not been preserved in history.
The method of removing the plug is selected based on the neglect of the process. Soft and pasty wax plugs are removed by routinely rinsing the outer ear with warm water under pressure. For this, a syringe without a needle, a syringe, etc. is used.
Dry and hard sulfur plugs require initial softening (using hydrogen peroxide or cerumen) followed by rinsing.
Plugs that cannot be softened can be removed with a special medical instrument.
Prevention of the formation of sulfur plugs
To prevent the formation of sulfur plugs in the ears, otorhinolaryngologists at the K + 31 Clinic offer some simple tips:
- Proper care of the ears: for this you need to regularly wash the auricle with soap, the external auditory canal is washed only to the depth of penetration of the little finger, and cotton ear buds are used only outside;
- Limiting harmful effects of the environment: reducing the time spent in dusty, high humidity or excessively dry rooms.
- Timely treatment of diseases of the ear, temporomandibular joint and other pathologies that worsen the spontaneous evacuation of earwax or increase its secretion.
Following these rules will help to avoid the formation of sulfur plugs and will keep you healthy.

